Some Consequences of the Refraction of Light
Some Consequences of the Refraction of Light: Overview
In this topic, we will learn about the light refraction and its impact on image formation. It explains how the refraction of light through an object can alter the view of that object. We will also learn about how image formation works.
Important Questions on Some Consequences of the Refraction of Light
The thickness of a plane-convex glass lens in the middle is . Viewing from the flat side the thickness of the lens at the centre will appear (refractive index of glass is ) to be
A tank is filled with water to a height of . Find the apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope. Refractive index of water is .
The relation between refractive index of a medium, real depth and apparent depth is
Difference between optically denser medium and optically rarer medium.
State two examples of phenomenon of refraction of light in everyday life situations.
The phenomenon that takes place due to the bending of light when it travels from medium to another is known as
How is apparent depth and real depth related to refractive index?
A water pond appears to be deep. If the refractive index of water is . Determine the actual depth of the pond in metre.
A fish seems to be at a depth of from the surface. What is the actual distance from the surface in ? (Refractive index of water is )
is equal to the ratio of real depth to the _____.
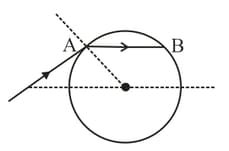
What should be the angle of incidence at A of the spherical glass placed in air so that so that grazing emergence of light ray takes place at
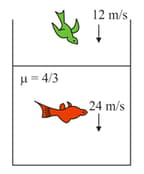
A fish and a bird are moving as shown in figure. Find the velocity of bird as observed by fish.
The apparent depth of needle lying at the bottom of the tank which is filled with water to a height of is measured by a microscope to be . If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index to the same height as earlier, compute the displacement of the microscope needed to establish focus on the needle again.
If light is refracted from a plane surface while passing from a denser medium to rarer medium, then which of the following statements is/are correct about it. [ is critical angle]
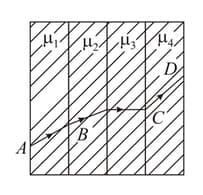
A ray of light passes through four transparent media whose surfaces are parallel to each other with refractive indices . If the emergent ray, is parallel to the incident ray , then, which of the following relations should be correct?
The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank, which is filled with water of refractive index to a height of is measured by a liquid of refractive index up to the same height. What distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
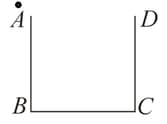
A cubical vessel has opaque walls. An observer (dark circle in the figure below) is located, such that she can see only the wall, , but not the bottom. Nearly to what height should water be poured, so that she can see an object placed at the bottom at a distance of, , from the corner, ? Refractive index of water is, .
The angles of incidence and refraction of a monochromatic ray of light of wavelength at an air-glass interface are and respectively. A parallel beam of light with a small spread in wavelength about a mean wavelength is refracted at the same air-glass interface. The refractive index of glass depends on the wavelength where a and b are constants. Then the angular speed in the angle of refraction of the beam is
A girls sees through a circular glass slab (refractive index ) of thickness and diameter to the bottom of a swimming pool. The refractive index of water is . The bottom surface of the slab is in contact with the water surface.
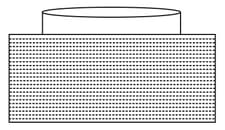
The depth of the swimming pool is . The area of the bottom of the swimming pool that can be seen through the slab is approximate-
A horizontal parallel beam of light passes through a vertical convex lens of focal length, and is then reflected by a tilted plane mirror so that it converges to a point . The distance is .
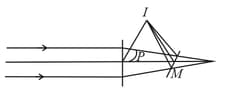
is a point at which the axis of the lens intersects the mirror. The distance is . The angle which the mirror makes with the horizontal is,
