Radioactivity
Radioactivity: Overview
This topic describes the concepts of radioactivity and the laws of radioactive decay. It also explains the process of alpha, beta, and gamma decay.
Important Questions on Radioactivity
Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio . The ratio of their nuclear radii would be:
The plot of the activity of a radioactive species versus time would be:
How long will a radioactive isotope, whose half life is years, take for its activity to reduce to of its initial value?
Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio . The ratio of their nuclear radii is:
In decay, the terms half-life period and decay constant is used. The relationship between the two is
The half life of a radioactive substance isminutes. In how much time, the activity of substance drops to of its initial value?
The half-life of a radioactive nucleus is years. The fraction of the original sample that would decay in years is :
Two radioactive elements and initially have same number of atoms. The half life of is same as the average life of . If and are decay constants of and respectively, then choose the correct relation from the given options.
The half life of a radioactive substance is . The time taken, for disintegrating part of its original mass will be:
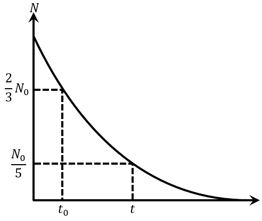
The graph shows the variation of the number of radioactive atoms left undecayed with time. The time corresponding to is:
Following statements related to radioactivity are given below :
(A) Radioactivity is a random and spontaneous process and is dependent on physical and chemical conditions.
(B) The number of undecayed nuclei in the radioactive sample decays exponentially with time.
(C) Slope of the graph of (no. of undecayed nuclei) vs. time represents the reciprocal of mean life time .
(D) Product of decay constant and half-life time is not constant.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A radioactive nucleus undergoes spontaneous decay in the sequence
,
where is the atomic number of element . The possible decay particles in the sequence are:
Which of the following is a radioisotope?
A scientist found a specimen in which the decay constant of nuclei and nuclei are and respectively. At the number of and nuclei were the same. The ratio of number of nuclei to that of nuclei will reduce to after a time interval of
Two radioactive materials and have decay constants and respectively. Starting with the same number of nuclei of and the ratio of the number of nuclei of remaining to that of remaining will be , after a time
You have a radioactive isotope that has a half-life of day. If you have atoms of this isotope, how long would you have to wait so that you will only have atoms left?
has a half life of years and its abundance in the atmosphere is in carbon atoms. A fresh sample of mole of collected from the atmosphere records a decay of atoms over a week. A large piece of old wood is burnt and mole of collected from it records a decay of atoms over a week. Then the age of the wood is close to
What are Radioisotopes? State Two Uses of Radioisotopes.
uranium, polonium are examples of radioactive materials.
Out of the following, which are radioactive substances?