Energy
Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Work-Energy Theorem, Potential Energy, Energy & Kinetic Energy etc.
Important Questions on Energy
An object of mass, is moving with a constant velocity, . How much work should be done on the object in order to bring the object to rest?
Assertion: If velocity of a moving body is increased to double, then its kinetic energy increases four times.
Reason: Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of velocity.
The explosion at Krakatoa is estimated to have released the energy equivalent to of TNT. The first nuclear detonation-the Trinity test -yielded an equivalent of of TNT. How many times more powerful was the explosion at Krakatoa?
A car travels along a flat road. It has of kinetic energy. Every second, air resistance and other frictional forces cause it to lose of energy. If the car is to travel at a constant speed, how much energy will the engine have to convert to kinetic energy every second?
A toy car has a kinetic energy of . It rolls up a slope and at the top it has of gravitational potential energy and of kinetic energy. How much energy has the car lost through friction?
When a driver wants to stop a car, he presses the brake pedal. The brakes applied, which use friction to slow the car to a stop. Which of the following energy transformations occurs as a car brakes?
A driver parks his car on a hill but forgets to put brakes on. The car starts to roll down the hill. Which of the following energy transformation occurs as the car rolls down the hill?
A body of mass is placed at a certain height from the surface of earth. If its potential energy is , then what will be its height with respect to earth's surface?
Loudspeaker converts electrical energy to _____ (sound/heat) energy.
There is a slight temperature difference between the waterfall at the top and at the bottom because
A stone of mass is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of . Calculate the potential energy (in joules) at the greatest height.
A body of mass has the momentum Calculate the kinetic energy and speed of the body.
A ball of mass slows down from a speed of to that of . Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the ball.
Calculate the kinetic energy of a body of mass and momentum (in joules)
A bullet of mass travels with a speed of . If it penetrates a fixed target which offers a constant resistive force of to the motion of the bullet, find the initial kinetic energy (in joules) of the bullet.
Two bodies A and B of masses and respectively have same kinetic energy. The ratio of velocity of A and B is:
If velocity of a moving body becomes one-fourth while the mass remains constant, the kinetic energy of the body
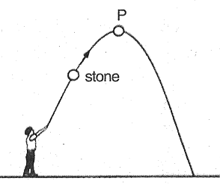
A stone is thrown upwards as shown in the diagram. When it reaches P, the _____ energy of the stone will be maximum.