Nutrient Cycles
Nutrient Cycles: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Water Cycle, Carbon Cycle, Biogeochemical Cycles, Phosphorus Cycle, Oxygen Cycle, Sulphur Cycle, Standing State, Sedimentary Nutrient Cycles and, Gaseous Nutrient Cycles
Important Questions on Nutrient Cycles
The main role of bacteria in the carbon cycle involves –
Which one of the following will accelerate phosphorus cycle?
In the given diagram, some labels are missing. Identify them and select the correct option:
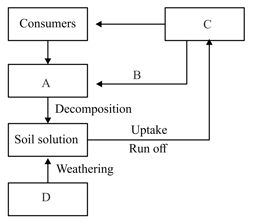
Correct statements among the following are:
I. Atmospheric input of phosphorous through rainfall is much smaller than carbon.
II. Gaseous exchange of phosphorous between organism and environment is negligible.
III. Herbivores and other animals obtain phosphorous through their foods.
IV. A considerable amount of carbon returns into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels.
Consider the following statements about carbon cycle and choose how many statements are correct?
(a) Atmosphere has of total global carbon.
(b) Decomposers contribute substantially to pool by their processing of waste materials and dead organic matter of land or oceans.
(c) carbon is fixed through photosynthesis annually.
(d) No respiratory input into atmosphere.
(e) Carbon constitutes of dry wt. of organisms.
Major utilisation of carbon from the atmosphere is through:
In an ecosystem, the cycling of nutrients is not known as
Assertion : Excess of sulphur reaches to reservoir pool.
Reason : Thiobacillus and Desulfovibrio convert elemental sulphur into the sulphate.
Study the cycle shown below and select the option which gives correct words for all the four blanks and .
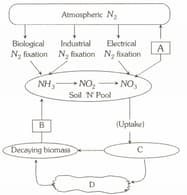
Which of the following is NOT true for the biogeochemical cycle according to the following cycle

Phosphorus of ocean becomes available to land plants due to
Phosphorus is mostly found in rocks in combination with
In water receiving regions, what does forest regulate
