Population Interactions
Population Interactions: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Commensalism, Parasitism, Mutualism, Predation, Amensalism, Scavenging, Ectoparasite, Brood Parasitism, Endoparasite, Protocooperation, Gause's Principle, Co-evolution, Phytophagous Insects and, Cryptic Coloration
Important Questions on Population Interactions
When an animals changes its body colour or body form and looks like another living organism, the phenomenon is called:
The egrets always forage close to where the cattle are grazing. The interaction between them can be called:
Which of the following interactions play a key role in keeping an eye on the number of the population?
Find the correct match of the organisms with the interaction they exhibit:
(a) Cuscuta growing on a shoe flower plant i)Brood Parasitism
(b) Mycorrhizae living on the roots higher plants. ii)Commensalism
(c) Clownfish living among the tentacles of a sea anemone. iii)Mutualism
(d) Koel laying her eggs in the crow’s nest. iv)Parasitism
Obligate parasites live on
Territoriality occurs as a result of
The symbiotic relationship of algae and fungus is found in
What is the difference between co-evolution and mutualism?
In an interaction among species A and species B, species A can show camouflage, chemical or morphological defence against species B. Species A is most likely to be:
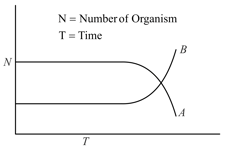
The following graph is the depiction of change in two populations (A and B) of herbivores in grassland with respect to time. The possible reason for these changes may be:
Species that are most effective at colonising new habitats show
Lizards in Caribbean Islands mostly feed on varieties of insects present in that area. However, different species of lizards live in different microclimatic zones or microhabitats that allow them to co-exist in a larger habitat area. This is termed as
The relationship between which among the following is an example of commensalism?
Animals have the innate ability to escape from predation. Examples for the same are given below. Select the incorrect example.
Association between sucker-fish (Remora) and shark is:
Sometimes parasites themselves are parasitised by other organism, such parasites known as
The function of aposematic colouration is to
Which of the following is paired incorrectly?
