Mendelian Disorders in Humans
Mendelian Disorders in Humans: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Thalassemia, Sickle-cell Anaemia, Cystic Fibrosis, Haemophilia, Colour Blindness, Phenylketonuria, Pedigree Analysis, Tay-Sachs Disease, Autosomal Dominant Disorders and, Mendelian Disorders
Important Questions on Mendelian Disorders in Humans
Choose the Mendelian disorder that is a sex-linked recessive disorder.
What would be the genotype of:
(i) An individual who is carrier of sickle cell anaemia gene but apparently unaffected.
(ii) An individual affected with the disease.
Which of the following species is rarely haemophilic?
Recently a girl baby has been reported to suffer from haemophilia. Her mother was not suffering from the disease. The genotype of her father would be:
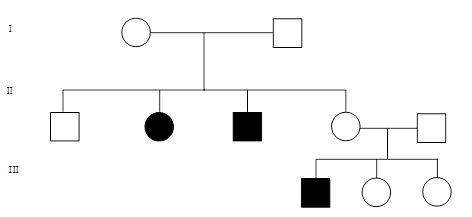
The trait can be described as:
The haemophilia is:
Sickle cell anaemia is characterised by
Genes of which one of the following is present exclusively on the X-chromosome in humans?
A female has two X chromosomes, one carrying allele for colour blindness and other for Haemophilia, and this female marries to a colourblind man. What is the percentage of offspring to get affected by both disorders?
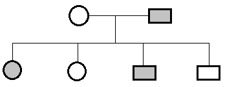
Find our the genotype of father and mother in given pedigree chart for autosomal recessive disorder.
In humans, attached earlobes are a dominant feature over free earlobes while hypertrichosis of the ear is a holandric (-linked) feature. A man with attached earlobes and extensive hair on pinna married a woman having free earlobes. The couple had one son with attached earlobes and hairy pinna, another son with free earlobes and hairy pinna and two daughters with attached earlobes. One of the daughters married a man with free earlobes and sparse hair on pinna. They had two sons. What would be the characteristics of their pinnae? What would be characteristic of their two daughters?
A red eyed male fruit is crossed with a white eyed female fruit fly. Work out the possible genotype and phenotype of F1 and F2 generation. Comment on the pattern of inheritance in this cross.
A group of researchers performed a genetic survey of two different human populations, one living in a deep tropical forest and the other in a faraway metropolitan city of the same country. Their haemoglobin genes were analyzed and classified as normal or sickle cell anaemic. Five years later, the same group of researchers performed another survey for the occurrence of malaria in these two populations. The reports are tabulated as follows:
| Year | Forest | city |
| Total number of individuals in the population | ||
| Number of individuals who made malaria in the last years | ||
| Number of individuals who died due to anaemia in the last years |
| Year | Forest | city |
| Total number of individuals in the population | ||
| Number of individuals with normal haemoglobin gene | ||
| Number of individuals with sickle cell anaemia gene |
Sickle cell anaemia manifests in an individual because of a defective haemoglobin gene. Assuming that the rate of exposure to malarial parasites remains constant both in forest and in the city during the last years, and other compounding factors do not exist, which of the following statement(s) is/are most likely to be correct?
Choose the correct the combination.
| Group I | Group II | ||
| P. | Phenylketonuria | i. | Melanin synthesis |
| Q. | Albinism | ii. | Conversion of Phenylalanine to Tyrosine |
| R. | Homocystinuria | iii. | Tyrosine degradation |
| S. | Argininemia | iv. | Methionine metabolism |
| v. | Urea synthesis |
Which of the following is/are sex-linked disease?
The progeny of normal woman and colour-blind father will be
Which of the following statements are correct?
Which one of the following disorders and characteristic is correctly matched
Which ONE of the following Mendelian diseases is an example of -linked recessive disorder?
Identify the odd one among the following disorders:
