Reflex Action and Reflex Arc
Reflex Action and Reflex Arc: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Cranial Nerves, Peripheral Nervous System, Vagus Nerve, Ganglia, Spinal Nerves, Reflex Arc, Reflex Action, Parasympathetic Nervous System, Facial Nerve, Trigeminal Nerve, Somatic Nervous System and, Oculomotor Nerve
Important Questions on Reflex Action and Reflex Arc
Mention three branches of the autonomic nervous system.
Which of the following cranial nerve is involved in the movement of the tongue?
What are the functions of the twelfth cranial nerve arising from the medulla?
Which of the following explains twelfth cranial nerve?
What happens if there is damage to the accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI)?
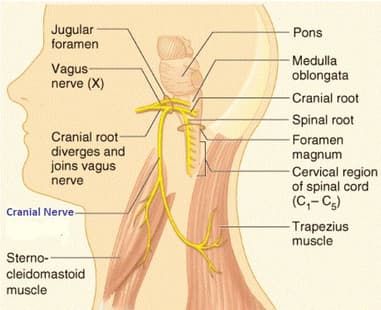
The eleventh cranial nerve is a motor nerve, supplies to the neck and upper back regions, running between occipital and temporal bones.
Which of the following is correct for the cranial nerve (shown in blue colour) in the given picture?
Which of the following represents the eleventh cranial nerve?
The motor fibers of a mixed nerve arising from the medulla and ends in the parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary salivary glands is:
The sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve transmit impulses to the _____ (medulla/ taste buds of the tongue).
Nerve fibers of the seventh cranial nerve end in sublingual salivary glands are:
The seventh cranial nerve is known as facial nerve, and it is a _____ (mixed nerve/sensory nerve).
The sensory fibers of the seventh cranial nerve extends to the pons through the Gasserian ganglion.
Motor fibers of the facial nerve end in all except:
Explain first cranial nerve.
The olfactory nerve is the first and shortest cranial nerve consisting of sensory nerve fibers to sense smell.
Olfactory nerves:
Optic nerve has no role in the movement of eyeball.
Explain the path of optic nerve.
Optic nerves regulate the movement of _____ . (eyeballs/pinnae)