Female Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Female Reproductive System, Uterus, Clitoris, Cervix, Endometrium, Labia Minora, Labia Majora, Isthmus, Mons Pubis, Female External Genitalia, Oviducts, Myometrium, Ampulla, Perimetrium, Human Ovary and, Vagina
Important Questions on Female Reproductive System
In humans, the female reproductive cell is:
Which of the following is correctly matched?
The primary follicles are scattered in the
Identify the correct statement.
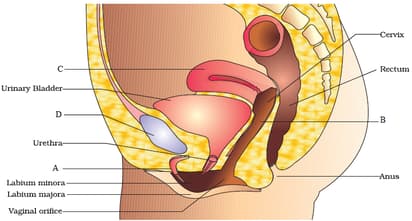
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
A - Contains two erectile tissues and urethra.
B - Lined by stratified, squamous, non-keratinised epithelium.
C - Almond shaped structure, 2-4 cm in length.
D - Hyaline cartilage which relaxes during parturition under activity of relaxin hormone.
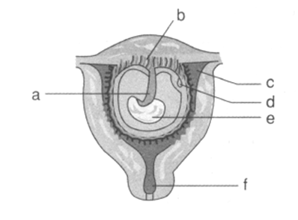
What does 'b' represent in the figure?
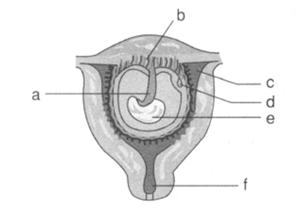
What does 'a' represent in the figure?
What does 'd' represent in the figure?
Hymen can be torn or broken by
(i) First coitus
(ii) Sudden fall or jolt
(iii) Horse riding
(iv) Cycling
(v) Insertion of a vaginal tampon
Which facts about the uterus (in human females) is true?
Find out the incorrect statement about ovaries.
The female reproductive system along with a pair of mammary glands is integrated structurally and functionally to support the process of
The upper meeting point of the two labia minora possesses a small finger-like structure:
The part of the oviduct near the ovary is the funnel-shaped:
The clitoris is a tiny finger-like structure that lies at the upper junction of the two labia minora above the urethral orifice. It is found to be:
Assertion: The uterus is shaped like an inverted pear.
Reason: The inner glandular layer lining the uterine cavity is called myometrium.
In human beings, the outer serous layer of the uterus is called _______.
An average menstrual cycle is of how many days.
Name the part of female external genitalia that includes cushion of fatty tissue covered by skin and pubic hair.
