Properties of Acids and Bases
Properties of Acids and Bases: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Properties of Acids, Properties of Bases, Reactions of Acid with Metals, Acid-base Neutralisation Reactions: Salts Formation and, Reactions of Metal Carbonates with Acids
Important Questions on Properties of Acids and Bases
Name the gas that was released during the limestone reaction with acids.
The colour of the filtrate formed by the reaction of concentrated sulphuric acid with manganese dioxide is _____.
A diagram of the reaction of Zinc with acid is given below.
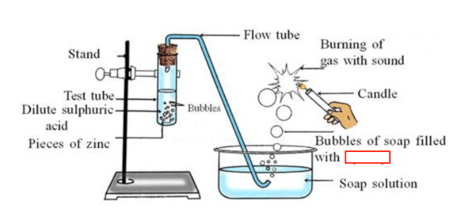
During this reaction, a gas is evolved. Write the name of the gas. (Sulphur dioxide/ Hydrogen)
When is added to of , the of the resulting solution will be ___.
When magnesium and hydrochloric acid react, they produce_____________.
Salts are made up of molecules.
What gas is produced when magnesium is made to react with hydrochloric acid?
Complete the following reaction:
Name the gas that is produced when an acid reacts with a metal? (Hydrogen / Oxygen / Carbon dioxide)
1 g of fuming (oleum : It is a mixture of concentrated saturated with and having formula ) is diluted with This solution is completely neutralized by 26.7 mL of 0.8 N NaOH. Find the percentage of free in the oleum
The heat of neutralization of four acids and are and , respectively, when they are neutralized by a common base. The acidic character obeys the order:
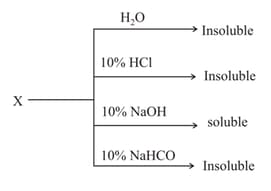
Which of the following reagents will be fruitful for separating a mixture of nitrobenzene and aniline?
The heats of neutralization of and are and per equivalent respectively. The correct increasing order of acid strength is
The pairs of compounds which cannot exist together in aqueous solution are: