Chemical Properties of Group 1 and 2 Elements
Chemical Properties of Group 1 and 2 Elements: Overview
In this topic, we will come across the chemical properties of Group 1 and Group 2 elements in detail. Some key characteristics and reactions will also be discussed related to them.
Important Questions on Chemical Properties of Group 1 and 2 Elements
One mole of magnesium nitride on the reaction with an excess of water gives:
Several blocks of magnesium are fixed to the bottom of a ship to
(potassium super oxide) is used in oxygen cylinders in space and submarines because it.
Better method for preparation of , among the following is
The compound which does not exist is
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Lithium and Magnesium do not form superoxide
Statement II : The ionic radius of is larger than ionic radius of In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the questions given below :
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the questions given below :
Consider the following reaction:
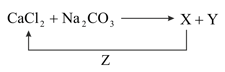
Which compound does not exist from the following?
Read the following two statements
Statement I: Ionic radius of is greater than
Statement II: Lithium and magnesium can't form superoxide
Arrange the hydrides of group I in increasing order of their stability.
The set of metals that can react with water even in cold conditions are
The pair of elements that form both oxides and nitrides, when burnt in air are
Ine metal which dissolves in liquid ammonia to give a blue-black solution due to formation of solvated electron is
The strongest reducing agent is
Which among the following is the strongest reducing agent?
M can be
In all oxides, peroxides and super oxides, the oxidation state of alkali metals is-
The set of metal halides in which all the members form hydrates is:
When a solution of alkaline earth metal in liquid ammonia is evaporated:
Alkaline earth metals react with halogens to form metal halides.
