Condensation Polymers
Condensation Polymers: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Bakelite, Esterification, Vulcanisation of Rubber, Polyamides, Condensation Polymers, Nylon-6, Mechanism of Esterification, Nylon-6, 6, Butadiene-Styrene Rubber, Linear Polymers and, Thermosetting Plastics
Important Questions on Condensation Polymers
What are the branched chain polymers? Give examples.
What are the monomers of styrene butadiene?
Vulcanisation improves elasticity of rubber. What is meant by the term vulcanisation?
The following formula represent the section of polymer, A.
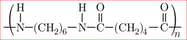
Suggest the structures of the monomers from which it is formed.
Write the chemical names of nylon- and chloroprene.
The process involving heating of rubber with sulphur is called
Give one physical property of the cross-linked synthetic polymer.
Write the names of monomers of the given polymer :
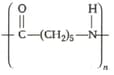
Write the names of monomers of the given polymer :
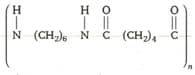
Write the names of the monomers for the polymer : Nylon--nylon-.
Write the names of the monomers for the polymer bakelite.
Give the monomers of the polymer bakelite.
What is the common name of the polymer obtained by the polymerisation of caprolactam? Is it addition polymer or condensation polymer?
What are polyamide? Give one example of a polyamide and name its monomers.
Which of the following is a polyamide molecule?
Nylon is prepared from adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. Which one of the following statement is not true? Nylon is an
The fibre obtained by the condensation of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid is
The polymer formed by the condensation of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid is
Classify the following as linear, branched or cross-linked polymer-
Polythene
