Group 16 (Oxygen Group) Elements
Group 16 (Oxygen Group) Elements: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Ozone, Sulphuric Acid, Sulphur Dioxide, Oleum, Structure of Sulphur Dioxide, Structure of Ozone, Uses of Sulphuric Acid, Preparation of Sulphuric Acid by Contact Process, Allotropes of Sulphur and, Rhombic Sulphur
Important Questions on Group 16 (Oxygen Group) Elements
The chemical formula of oleum is .
The chemical formula of _____ (soda/oleum) is .
The chemical formula of oleum is .
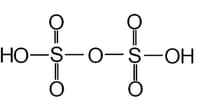
The structure is shown below is of _____ (oleum/soda).
Write the chemical formula of oleum.
Explain the use of sulphur dioxide in the contact process?
What are the uses of rhombic sulphur?
From the two allotropes of sulphur, Rhombic sulphur and Monoclinic sulphur, which is more stable?
An allotrope of sulphur which is stable at room temperature is _____ sulphur.
Which is the most stable allotrope of sulphur?
When a flower bleached by _____ is brought in contact with air and light the colour of the flower is restored.(sulphur dioxide/carbon dioxide)
The catalyst used in the preparation of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide is _____. (Manganese dioxide / Calcium oxide)
Sodium sulphate can be distinguished from sodium sulphite by using
On addition of concentrated to a chloride salt, colourless fumes are evolved but in case of an iodide salt, violet fumes come out. This is because
Which of the following will not be obtained when is mixed with water:
acts as a bleaching agent in presence of moisture. This is due to the _____ nature of . (reducing / oxidising)
Brief about the stability of monoclinic sulphur.
Write a short note on the allotropic forms of sulphur such as plastic sulphur, colloidal sulphur and milk of sulphur.
The elements, selenium and tellurium occur as metal selenides and tellurides in
Name the synthetic radioactive element of Group- of the periodic table.