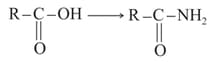Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives
Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Esterification, Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction, Reduction of Carboxylic Acids, Decarboxylation of Carboxylic Acids, Soda lime Decarboxylation, Acidity of Carboxylic Acids and, Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Important Questions on Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives
The correct increasing order of acidic strength of the following compounds is
benzoic acid
nitro benzoic acid
, dinitrobenzoic acid
methoxybenzoic acid
Identify A to D in the following sequences of operations:
The reagents that can be used to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds would be:
(i) Propanal and Propanone
(ii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of followed by treatment with a saturated solution of gives –
Among the following acids which has the lowest value?
A liquid was mixed with ethanol and a drop of concentrated H2SO4 was added. A compound with a fruity smell was formed. The liquid was:
A liquid was mixed with ethanol and a drop of concentrated H2SO4 was added. A compound with a fruity smell was formed. The liquid was:
Which amongst the following compounds has the highest acid strength?
Effervescence takes place when sodium carbonate solution is added to
The product formed when two equivalents of reacts with acetyl chloride followed by hydrolysis is
The following transformation
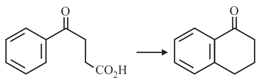
can be carried out in three steps. The reagents required for these three steps in their correct order, are:
Which is the strongest acid?
In the equation the compound is :
The product obtained when acetic acid is treated with is:
Fischer esterification is:
What are and in the above reaction?
The correct increasing order of acidities is:
The order of acidic strength of following acids is
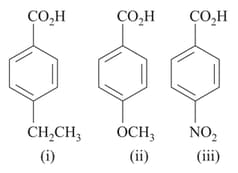
The correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following acids is:
1) Trichloro acetic acid.
2) Trifluoro acetic acid.
3) Acetic acid.
4) Formic acid.
For the following conversion which reagent can be used :