Isomerism in Organic Compounds
Isomerism in Organic Compounds: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Isomerism, Optical Isomerism, Geometrical Isomerism, Enantiomers, Tautomerism, Stereoisomerism, Structural Isomerism, Chain Isomerism, Metamerism, Types of Isomerism, Degree of Unsaturation and, Position Isomerism
Important Questions on Isomerism in Organic Compounds
When an optically active compound is placed in a 10 dm tube, it is present 20 gm in a 200 mL solution rotates the PPL by 30o. Calculate the angle of rotation and specific angle of rotation if above solution diluted to 1 litre.
On chlorination of propane, the number of products having the formula is
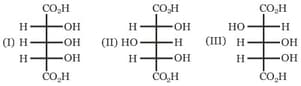
Which of the above compounds are enantiomers?
Dextrorotatorypinene has a specific rotation . A sample of pinene containing both the enantiomers was found to have a specific rotation value . The percentages of the (+) and (-) enantiomers present in the sample are, respectively.
Dextrorotatorypinene has a specific rotation . A sample of pinene containing both the enantiomers was found to have a specific rotation value . The percentages of the (+) and (-) enantiomers present in the sample are, respectively.
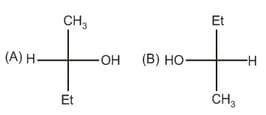
Relation between given pair is:
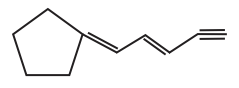
The number of cis-trans isomer possible for the following compound
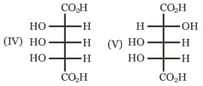
Which are the pairs of enantiomers and diastereomers from the following
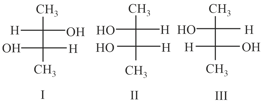
How many optically active stereoisomers are possible for butane-2, 3-diol?
The geometrical isomerism in oximes are called cis-trans isomers.
Draw the geometrical isomers of acetaldoxime.
Which isomerism is shown by the following
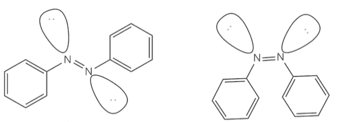
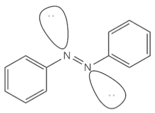
The given structure represents the Z-azobenzene.
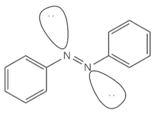
The given structure represents the E-azobenzene.
Draw the E-Z geometrical isomers of azobenzene.
Give an example of dyad system of tautomerism.
Hydrogen cyanide can exhibit dyad system of tautomerism.
Which of the following compounds which exhibits a dyad system of tautomerism.
Represent the different forms of triad tautomers.
Give an example of triad tautomerism.
