Isomerism in Alkanes
Isomerism in Alkanes: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Isomerism in Alkanes, Chain Isomerism in Alkanes, Position Isomerism in Alkanes, Relative Stability of Conformations, Conformational Isomerism in Alkanes and, Newman Projections of Alkanes
Important Questions on Isomerism in Alkanes
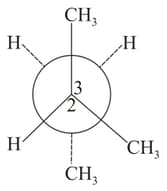
is rotated bond. The resulting conformer is
Isomers which can be interconverted through rotation around a single bond are
contains X number of allylic hydrogen and contains Y number of allylic hydrogen.The number of structural isomers of are
Which among the following is an isomer of propanol?
The number of primary, secondary, teritary and quanternary carbons in neopentane are respectively
Which of the following is the most preferred conformation of ethane molecule
What is incorrect order of stability?
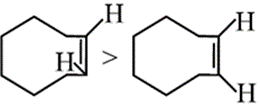
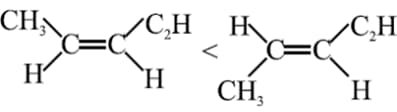
Boat form of
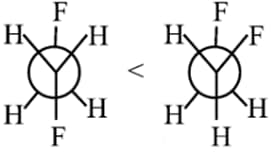
Gauche form of succine acid > Anti from of succinic acid
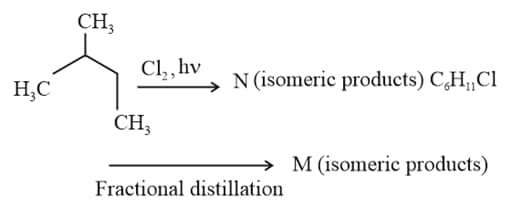
What is the minimum number of carbon atoms of an alkane must have to form an isomer?
The conformation of isopentane having maximum torsional and maximum Van der waal strain is
How many conformational isomers of butane are chiral.
An unsaturated hydrocarbon on complete hydrogenation gives 1-isopropyl - 3 - Methyl cyclohexane, after ozonolysis it gives one mole of formaldehyde, one mole of acetone and one mole of acetone and one mole of 2,4-dioxohexanedial. The possible structures of hydrocarbon are
The most stable configuration of succinic acid in Newmann Projection is:
For which of the following molecules, Gauche form is more stable than Anti.
For which of the following molecules, Gauche form is more stable than Anti.
For the given Newman projection,
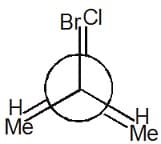
The configuration is
Which of the following will have least hindered rotation about carbon-carbon single bond?
Identify the most stable conformation.
Identify the most stable conformation -