Drug Action and Development of New Drugs
Drug Action and Development of New Drugs: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Inhibitor, Enzyme Inhibitors, Clinical Trials, Competitive Inhibitors, Drug Discovery, Drug Design, Preclinical Trials, Drug Development Process and, NCE (New Chemical Entity) Related to Drug
Important Questions on Drug Action and Development of New Drugs
Define inhibitor of a reaction.
Select whether the following statement is True or False:
A competitive inhibitor is a compound that bears a structural resemblance to a particular substrate, and thus it competes with that substrate for binding at the active site of an enzyme.
Describe the role of competitive inhibitors in catalytic action.
Write about the importance of post-clinical studies of a drug.
Clinical drug trials are used to determine
Define clinical trials of a drug.
What are preclinical trials?
Write about the process involved in preclinical trials related to drug design?
The process of drug design relies on knowledge about drug-receptor interactions.
What is drug design?
The process of drug delivery is :
What is drug discovery?
New chemical entity is the lead compound formed in the drug development process.
Define new chemical entity (related to drug).
Write about the first step involved in the drug development process?
What are the different steps involved in drug development process?
Taxotere (docetaxel) is an anticancer drug that can be synthesised using chiral auxiliaries. Suggest how the presence of unwanted stereoisomes in a drug might affect its pharmacological activity?
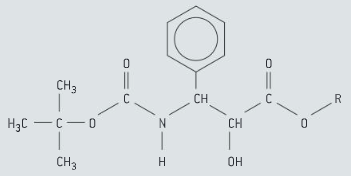
Describe the use of chiral auxiliaries to synthesise the desired enantiomer of a drug.
Discuss the importance of chirality in drug action.
The drugs which interact with target biomolecules are called _____.
