Electronic Effects
Electronic Effects: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Inductive Effect, Hyperconjugation, Mesomeric Effect, Electromeric Effects, Resonance Effect, Bond Order, Bond Length, Resonance Energy, Delocalised Electrons, Resonating Structures and, Conditions for Resonance
Important Questions on Electronic Effects
Which of the following compounds has maximum electron density in ring ?
List the following compounds in the order of decreasing reactivity towards nucleophilic attack.
The correct stability order of the following resonating structures is:
Number of resonance structures possible for anilinium ion are___?
The image below shows different benzene derivates that give mononitration product at ortho, meta and para positions along with the rate of nitration relative to benzene.
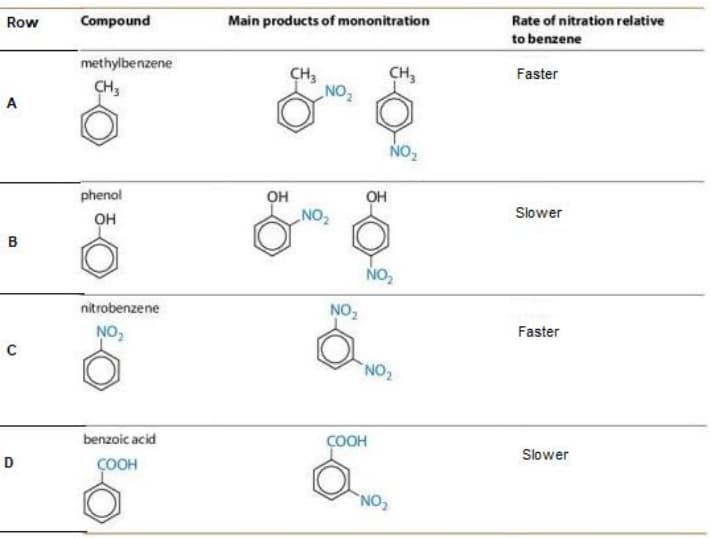
Which of the following row shows atleast one INCORRECT description about the reaction?
What is the correct order of decreasing stability of following carbocations?
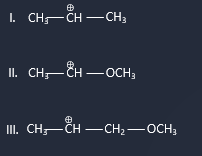
Which is more stable tropylium ion or benzene ?
What is dancing resonance ?
What is the order of effect.
Why allylic and benzylic carbocation are more stable than tertiary carbocation?
The displacement of electrons in a multiple bond in the presence of attacking reagent is called
Which of the indicated hydrogen in the following is most acidic :
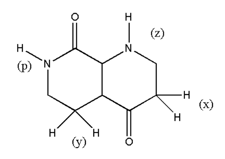
Which of the following have negative mesomeric effect?
Which of the following have negative mesomeric effect?
What is bond order? Calculate bond order for nitrogen molecule.
Describe negative mesomeric effect.
Which of the following statements is correct?
Why are pi bonds more reactive than pi electrons are more reactive than sigma electrons?
Benzene undergoes an electrophilic addition reaction.
Why benzene does not undergo electrophilic addition reaction?
