Quantitative Analysis of Organic Compounds
Quantitative Analysis of Organic Compounds: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Kjeldahl's Method, Quantitative Analysis of Organic Compounds, Dumas Method, Estimation of Carbon and Hydrogen, Estimation of Nitrogen, Estimation of Phosphorus, Estimation of Sulphur and, Estimation of Oxygen
Important Questions on Quantitative Analysis of Organic Compounds
In Carius tube, an organic compound ' ' is treated with sodium peroxide to form a mineral acid ' '. The solution of is added to ' ' to form a precipitate ' '. ' ' is used for the quantitative estimation of an extra element. ' ' could be
An organic compound on combustion gives . If the percentage of in given organic compound is , the percentage of hydrogen will be?
When a hydrocarbon undergoes complete combustion it requires equivalents of oxygen and produces equivalents of water. What is the molecular formula of ?
A gas mixture has propane and butane . At is produced when mixture is completely oxidised by excess of . If only propane is oxidised then produced consume for complete neutralisation. The mass% of in mixture is (nearest integer)
During estimation of nitrogen present in an organic compound by Kjeldahl's method, the ammonia evolved from of the organic compound neutralised of . If of the organic compound is used in the Duma's method, then of nitrogen at pressure. The value of is
(Aquesous tension at is and .
of hydrocarbon as exploded in excess of air. After cooling, there was a contraction in volume of and after treatment with , there was a further reduction of . The formula of hydrocarbon is . The value of is
Nitrogen present in of a substance was completely converted to ammonia which was neutralised by . Calculate the percentage of nitrogen.
Consider the following reaction.
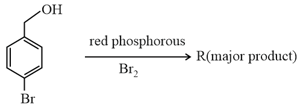
On estimation of bromine in of using Carius method, the amount of formed (in ) is____[Given: Atomic mass of ]
A mixture of g formic acid and oxalic acid is treated with concentrated . The evolved gaseous mixture is passed through pellets. Weight () of the remaining product at will be.
Which of following statement is correct
How does organic compounds react with excess of oxygen in presence of ?
How does carbon react with excess of oxygen?
Write the reaction for the conversion of sulphur to barium sulphate.
Write the reactions involved in the estimation of sulphur in an organic compound.
In a Carius method, of organic compound on treating with silver nitrate gives of . Calculate the percentage of chlorine in the given organic compound.
In Carius method of estimation of halogens, of an organic compound gave of . The percentage of bromine in the compound is : (atomic mass )
Carius method is used to estimate which of the following compounds?
Carius method is used for the estimation of halogen. of an organic compound gave of silver bromide. Percentage of bromine present in the compound is
Describe the setup for Carius method for the mass of halogens.
In quantitative analysis of carbon and hydrogen in an organic compound, let the mass of organic compound be , mass of water and carbon dioxide produced be and respectively. The percentage of carbon is given as:
