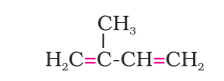Natural and Synthetic Rubbers
Natural and Synthetic Rubbers: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Vulcanisation of Rubber, Neoprene, Isoprene, Natural Rubber, Synthetic Rubbers, Buna-S, Buna-N, Butadiene-Styrene Rubber, Properties of Rubber, Preparation of Synthetic Rubbers and, Properties of Synthetic Rubbers
Important Questions on Natural and Synthetic Rubbers
How will you prepare butadiene-styrene rubber?
Butadiene-styrene rubber is prepared by the copolymerisation of butadiene and styrene.
Write some uses of butadiene-styrene rubber
Compare between synthetic and natural rubbers.
Give any two properties of synthetic fibres.
_____ are usually more water, stain, heat and chemical resistant.
Natural rubber is any vulcanisable rubber like polymer, which is capable of getting stretched to twice its length.
_____ is resistant to the action of petrol, lubricating oil and organic solvents.
Neoprene or polychloroprene is formed by the free radical polymerisation of chloropropane and it is used in making oil seals, tank lining, etc.
Which of the following structures represent repeating units of neoprene polymer?
Which of the following is the monomer of natural rubber?
The above image is the structure of monomeric unit of natural rubber(-methyl--butadiene), whose common name is _____.(Isoprene/chloroprene)
The monomer units of polymer Buna-N.
Vulcanization of rubber is a process of improvement of the rubber elasticity and strength by heating it in the presence of nitrogen.
Copolymerization of and acrylonitrile gives
Vulcanisation improves elasticity of rubber. What is meant by the term vulcanisation?
Give the reaction involved in the formation of Buna-S.
The process involving heating of rubber with sulphur is called