Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Photoelectric Effect, Photoelectrons, Threshold Frequency, Stopping Potential, Work Function, Threshold Wavelength and, Characteristics of Photoelectric Effect
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect
The energy absorbed by each molecule of a substance is and bond energy per molecule is What will be the kinetic energy of the molecule per atom?
Light of wavelength , shines on a metal surface with intensity , and the metal emits electrons per second of average energy . What will happen to and if is doubled?
A certain metal has a work function of . It is irradiated first with of light and later with of light. Among the following, the correct statement is: [Given:Planck constant Speed of light ]
Ultra-violet light is shone on a zinc surface and photoelectrons are emitted. The graph shows how the stopping potential varies with frequency
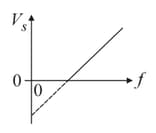
Planck's constant may be determined from the charge of an electron multiplied by
A light of frequency when falls on a metal plate emits electrons that have double the kinetic energy compared to the kinetic energy of emitted electrons when frequency of falls on the same plate. The threshold frequency of the metal in is
Which of the following results is not true about photoelectric effect?
If the work function for Caesium atom is , find the approximate value of its threshold wavelength.
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is found to be when the metal is irradiated with radiation of frequency . The threshold frequency of the metal is:
In photoelectric effect, the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons increases linearly with the
Photoelectric work function of a particular metal is . If a light having a wavelength of falls on the metal, then find out the approximate speed of the photoelectron emitted:
The factor on which the number of photoelectrons emitted per unit time depends in the photoelectric effect is
What will be the ratio of maximum kinetic energies of the photoelectrons on irradiation of metal with radiations of frequencies and respectively? Given the threshold frequency of a metal is .
Determine the work function for the photoelectric emission. If threshold wavelength for ejection of electron from metal is .
Data required for calculation:
$\epsilon_{0}=8.85 \times 10^{-12} \mathrm{C}^{2} / \mathrm{Nm}^{2}$
$h c=12400 \mathrm{eV}$Å
$R=\frac{25}{3} \mathrm{J} / \mathrm{mol}-\mathrm{K}$ or $R=2 \mathrm{cal} / \mathrm{mole}-\mathrm{K}$
An experimental setup of verification of photoelectric effect is shown in the diagram. The voltage across the electrodes is measured with the help of an ideal voltmeter, and which can be varied by moving jockey J on the potentiometer wire. The battery used in potentiometer circuit is of $20 \mathrm{V}$ and its internal resistance is $2 \Omega .$ The resistance of $100 \mathrm{cm}$ long
potentiometer wire is $8 \Omega$
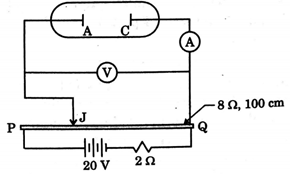
The photocurrent is measured with the help of an ideal ammeter. Two plates of potassium oxide of area $50 \mathrm{cm}^{2}$ at separation $0.5 \mathrm{mm}$ are used. in the vacuum tube. Photo-current in the circuit is very small so we can treat potentiometer circuit an independent circuit. The wavelengths of various colours are as follows:
| Light | in Å |
| 1 Violet | 4000-4500 |
| 2 Blue | 4500-5000 |
| 3 Green | 5000-5500 |
| 4 Yellow | 5500-6000 |
| 5 Orange | 6000-6500 |
| 6 Red | 6500-7000 |
When radiation falls on the cathode plate a current of $2 \mu \mathrm{A}$ is recorded in the ammeter. Assuming that the vacuum tube setup follows ohm's law, the equivalent resistance, of vacuum tube operating in this case when jockey is at end $P$.
Find the number of electrons that appeared on the surface of the cathode plate, when the jockey is connected at the end of the potentiometer wire. Assume that no radiation is falling on the plates.
Einstein's photoelectric equation states that . In this equation, refers to
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is plotted against the frequency v of the incident light. The resulting curve is a straight line which makes an angle with the v-axis. Then will be equal to
(Here
work function of the surface)
Which of the following plot is correct about the kinetic energy of photoelectrons?
When photons of energy strike the surface of a metal , the ejected photoelectrons have maximum kinetic energy, (expressed in ) and de Broglie wavelength The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons liberated from another metal by photons of energy If the de Broglie wavelength of these photoelectrons is then which is not correct?
