Determination of Order of Reaction
Determination of Order of Reaction: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Hit and Trial Method for Determining Order of a Reaction, Methods of Determination of Order of Reactions and, Determination of Order of a Reaction by Half Life Method
Important Questions on Determination of Order of Reaction
Consider a reaction . When concentration of both the reactants G and H is doubled, the rate increases by eight times. However, when concentration of G is doubled keeping the concentration of H constant, the rate is doubled. The overall order of the reaction is:
For a reaction, . What is order of reaction?
If 50 % of a reaction occurs in 100 second and 75 % of the reaction occurs in 200 second, the order of this reaction is:
The rate of the haemoglobin -carbon monoxide reaction,
has been studied at . The Concentration of reactants are expressed in
| Rate of disappearance of | ||
The rate constant for the reaction is . The value of is
The reaction between and follows the equation . The following data were observed:
| Initial rate of appearance of | ||
The value of the rate constant for the given reaction is:
The plot of concentration of a reactant vs time for a chemical reaction is shown below.
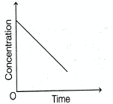
The order of this reaction with respect to the reactant is
A reaction occurs by the following mechanism:
(i)
(ii)
The net reaction is:
= constant, confirms that the order of the reaction is one.
= constant, confirms that the reaction is of: ( Initial concentration).
At particular concentration, the half life of the reaction is minutes. when the concentration of reactant becomes double half life becomes minutes, then what will be the order of the reaction ?
During kinetic studies of the reaction, the following results were obtained
product
How much time (in minutes) required to consume half of
| Experiment | Initial Rate of reaction | ||
| I | 0.10 | 0.20 | |
| II | 0.10 | 0.25 | |
| III | 0.20 | 0.30 |
The relative concentration of two samples of same substance is 200 and 50 respectively and their half-lives are 0.1 and 0.4 s respectively. What is the order of reaction?
For the reaction. , the reaction rate is doubled if the concentration of is doubled. The rate is increased by four times when the concentrations of both and are increased by four times. The order of the reaction is......
Which of the following is second-order reaction?
Example of a second order reaction among the following is:
At a temperature of , the half-life period of a gaseous reaction at an initial pressure of is . What is the order of the reaction, if the pressure is , the half-life period changes to ?
For a reaction between and , the rate law is given by . If we double the concentration of and half the concentration of , the ratio of the new rate to the earlier rate of reaction will be:
Consider the following reaction:
The half-life of reaction did not change when concentration of B alone was doubled. The rate increased by two times when the concentration of A alone was doubled. What is the unit of rate constant for above reaction?
Consider the reaction :
If the time taken for the partial pressure of gas A to fall from to is and
Concentration of reactant is plotted against time for the reactions of different order. Which of the following plot is/are correct ?
In the reaction, the time taken for the reaction of is twice the time taken for reaction of . The concentration of varies with reaction time as shown in the figure. The overall order of the reaction is: