Order of Reaction
Order of Reaction: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as First Order Reactions, Zero Order Reactions, Law of Mass Action, Order of a Reaction, Hit and Trial Method for Determining Order of a Reaction and, Methods of Determination of Order of Reactions
Important Questions on Order of Reaction
The half-life for decay of radioactive is 5730 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood has only 80% of the activity as found in living trees. The age of the artifact would be:
[Given: log 1.25 = 0.0969]
Consider a reaction . When concentration of both the reactants G and H is doubled, the rate increases by eight times. However, when concentration of G is doubled keeping the concentration of H constant, the rate is doubled. The overall order of the reaction is:
For the reaction the following data was collected. The order of the reaction is
| Initial rate | ||
Compounds and react according to the equation .
The initial rate of formation was determined at different initial concentrations of and The following results were obtained. The rate law for this reaction may be [All concentrations are in ].
| Exp. No. | Initial | Initial | Initial rate of formation of |
A reaction has rate constant Then find the ratio of to
If 50 % of a reaction occurs in 100 second and 75 % of the reaction occurs in 200 second, the order of this reaction is:
The rate of the haemoglobin -carbon monoxide reaction,
has been studied at . The Concentration of reactants are expressed in
| Rate of disappearance of | ||
The rate constant for the reaction is . The value of is
The reaction between and follows the equation . The following data were observed:
| Initial rate of appearance of | ||
The value of the rate constant for the given reaction is:
For the following elementary reaction, determine its order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constant:
For a reaction, , the rate is given by , hence, the order of the reaction is:
Order of a reaction with rate constant is :
The plot of concentration of a reactant vs time for a chemical reaction is shown below.
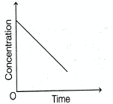
The order of this reaction with respect to the reactant is
A reaction occurs by the following mechanism:
(i)
(ii)
The net reaction is:
Rate constant of a chemical reaction is . Calculate the order of reaction?
= constant, confirms that the order of the reaction is one.
= constant, confirms that the reaction is of: ( Initial concentration).
For the reaction product
order of reaction is :-
At particular concentration, the half life of the reaction is minutes. when the concentration of reactant becomes double half life becomes minutes, then what will be the order of the reaction ?
Show that the time required for completion of a first order reaction is three times the time required for completion.
