Unit Cells, Two and Three Dimensional Lattices
Unit Cells, Two and Three Dimensional Lattices: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Crystal Lattice,Lattice Points,Unit Cell etc.
Important Questions on Unit Cells, Two and Three Dimensional Lattices
Silver crystallises with face-centred cubic unit cells and each side of the unit cell has a length of . Determine the radius of an atom of silver. (Assume that each face atom is touching the four corner atoms.)
Silver crystallises in a fcc lattice. The edge length of its unit cell is and its density is The atomic mass of silver on the basis of this would be:
The figures given below show the location of atoms in three crystallographic planes in a lattice.
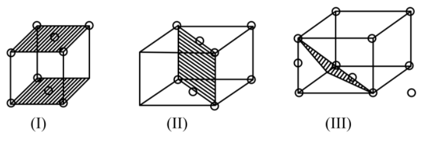
The planes in the unit cell have been highlighted in the diagram below choose the correct option.
Chromium metal crystallizes with a body centred cubic lattice. The length of the unit cell edge is found to be 287 pm. What would be the density of chromium in ?
Sodium metal crystallises in a body centred cubic lattice with the cell edge, What is the radius of a sodium atom?
The edge length of unit cell of a metal having molecular weight is which crystallizes in cubic lattice. If the density is then the radius of metal atom will be (in pm):
In face centred cubic (FCC) crystal lattice, edge length is 400 pm. The diameter of greatest sphere which can be fit into the interstitial void without distortion of lattice is
A substance crystallizes in a face centred cubic (FCC) lattice in which atoms occupy each corner of the cube and atoms occupy face centres of the cube composition of the substance is
In a Solid having the type structure, A atoms occupy the corners of the cubic unit cell. If all the face-centred atoms along one of the axes are removed, then the resultant stoichiometry of the solid is:
The coordination number of a metal crystallizing in a hexagonal close-packed structure is:
has bcc structure with edge length . The shortest inter ionic distance in between and is:
Potassium metal forms body-centered cubic crystals. What is the atomic radius of K and the volume occupied by the atoms in the unit cell if the side length of the unit cell of crystal is ?
What are Bravais lattices ?
What is fcc?
What fraction of one edge centred octahedral void lies in one unit cell of fcc?
A compound is formed by two elements A and B. The element B forms cubic close packed structure and atoms of A occupy of tetrahedral voids. If the formula of the compound is , then the value of is in option
Sodium metal crystallises in a body centred cubic lattice with unit cell edge length of . The radius of sodium atom is . (Nearest integer)
Number of crystal systems from the following where body centred unit cell can be found, is _____.
Cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, hexagonal, rhombohedral, monoclinic, triclinic
The correct relationships between unit cell edge length ‘’ and radius of sphere ‘’ for face-centred and body-centred cubic structures respectively are:
A compound is formed by two elements and The element forms cubic close packed arrangement and those of element occupy one third of the tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound?
