Electric Current and Drift Velocity
Electric Current and Drift Velocity: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Conductors, Electric Current, Drift Velocity, Electric Current Density, Relation between Drift Velocity and Electric Current, Mobility of Electron, Ohm's Law in Vector Form and, Relaxation Time of Electron
Important Questions on Electric Current and Drift Velocity
How do you find the average velocity of electrons in a wire?
Drift velocity of electrons is due to _____.
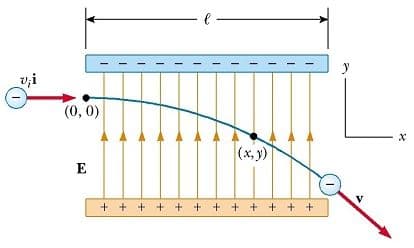
In the uniform electric field of , an electron is accelerated from rest. The acceleration of the electron is nearly (Charge of electron )
The acceleration of the electron while it is in the electric field is . Find the value of K.
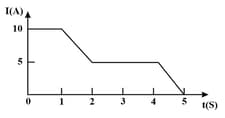
The current through an element is shown in the figure. Determine the total charge that passes through the element after in Coulombs.
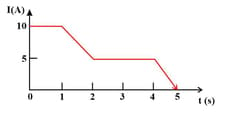
The current through an element is shown in the figure. Determine the total charge that has passed through the element at in Coulombs.
A current is flowing through the wire of diameter having drift velocity of electrons in it. What will be new drift velocity when diameter of wire is made
When temperature of a metal is increased, its conductivity
Which of the following statements is true about relaxation time?
With increase in temperature, the relaxation time of electrons in a material:
If current in a current carrying wire is , number of free electrons per unit volume is and area of cross section is . Drift velocity of electrons will be
A copper wire of cross-section area is carrying a current of . If the density of free electrons is . Calculate the drift velocity of free electrons.
Derive the relation between the drift velocity and electric field. What is mobility? Explain dependence of drift velocity and mobility.
Define drift velocity. On the basis of drift velocity derive Ohm's law ?
How much charge is accumulated when current is flowing through a conductor.
A copper wire of length and radius has electrical resistance of . The current density in the wire for an electric field strength of is
If current in a current carrying wire is , number of free electrons per unit volume is and area of cross section is . Drift velocity of electrons will be
A constant potential difference is applied between the ends of the wire. If the length of the wire is elongated such that the length becomes times, then the drift velocity of electrons will be
Cross - sectional area of a Copper wire is equal to area of a square of length . If this copper wire draws electric current, then find the drift velocity of free electron. Number density of electron in Copper wire is .
An electron is moving in a circular path of radius with a period of . The current constituted in the circular path is