Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity
Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Conductivity, Drift Velocity, Relation between Drift Velocity and Electric Current, Mobility of Electron, Relaxation Time of Electron and, Microscopic View of Electric Current
Important Questions on Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R).
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C), and (D) as given below.
Assertion: As the temperature of a conducting wire increases, the drift velocity of the electrons also increases.
Reason: With an increase in temperature, the average time of collision increases.
In a wire of cross-section radius r, free electrons travel with drift velocity v when a current I flows through the wire. What is the current in another wire of half the radius and of the same material when the drift velocity is 2V?
The average time between successive collisions for an electron for a conductor potential difference is . The mobility of electrons in metal conductors. (mass of the electron )
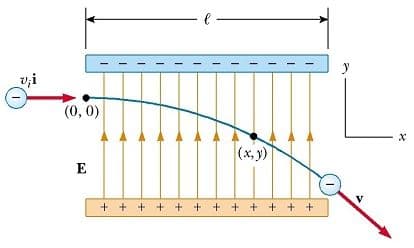
(a) Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area carrying a current of . Assume that each copper atom contributes roughly one conduction electron. The density of copper is , and its atomic mass is . (b) Compare the drift speed obtained above with, (i) thermal speeds of copper atoms at ordinary temperatures, (ii) speed of propagation of electric field along the conductor which causes the drift motion.
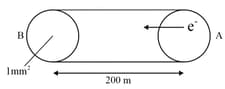
Find the time to move electron from A to B if and .
Define mobility.
The current in a copper wire is increased by increasing the potential difference between its ends. Which one of the following statements regarding the number of charge carriers per unit volume in the wire and , the drift velocity of the charge carriers is correct?
Calculate the value of average drift velocity through a copper wire having an area of cross-section, carrying a current of , If the number of electrons per cubic meter is .
Assertion
A current flows in a conductor only when there is an electric field within the conductor.
Reason
The drift velocity of electron in presence of electric field decreases.
Assertion: If an electron and proton enter an electric field with equal energy, then path of electron is more curved than that of proton.
Reason: Electron has a tendency to form curve.
Drift velocity of electrons is due to _____.
In the uniform electric field of , an electron is accelerated from rest. The acceleration of the electron is nearly (Charge of electron )
The negatively charged particle pictured below is accelerating in the direction indicated by the arrow, due to the influence of an electric field. Here the electric field is directed in the direction of motion of charged particle.
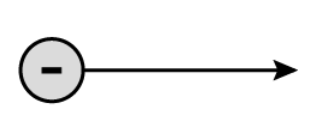
The acceleration of the electron while it is in the electric field is . Find the value of K.
A current is flowing through the wire of diameter having drift velocity of electrons in it. What will be new drift velocity when diameter of wire is made
Which of the following statements is true about relaxation time?
With increase in temperature, the relaxation time of electrons in a material:
Although free electrons are continuously in motion inside a conductor.Their average velocity is zero when no electric field is applied. Give reason.
Which of the following statement is not true for the motion of free electrons in the absence of electric field?
At normal room temperature, in a solid piece of metal, free electrons: