Electric Charge and its basic Properties
Electric Charge and its basic Properties: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Electron, Proton, Neutron, Electric Charge, Gold-Leaf Electroscope, Difference between Mass and Charge, Additivity of Charges, Quantization of Electric Charges and, Conservation of Electric Charges
Important Questions on Electric Charge and its basic Properties
In general, metallic ropes are suspended on the carriers which take inflammable material. The reason is
A body is having charge. If electrons move out of the body every second, then time after which the body becomes neutral will be approximately
A conductor is containing a charge of The numbers of electrons contained by the conductor are
A body is having charge. If electrons move out of the body every second, then time after which the body becomes neutral will be approximately
What are electrons?
Spheres A and B having equal masses are given charges and respectively. If after charging their respective masses are respectively
and , then relation of and will be _____.
Two identical light conducting balls having different charges, are being suspended freely. They are pushed towards each other as shown in the given figure.
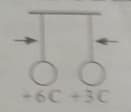
Which of the following options shows the correct position of the two balls, just after they touch each other?
Find the charge on an iron particle of mass if of electrons are removed from it.
The charge present in a doubly ionized helium atom is
A charge is to be divided on two objects. The value of charge on each object, such that force between the object can be maximum, would be
How many electrons must be removed from a body so that it may have the charge of
i.
ii.
High concentration of positive charges implies
How many electrons may be removed from a body so that it may have a charge (a) , (b) .
Four identical metallic sphere . Sphere carries charge , sphere carries , sphere and are uncharged. Sphere touches and sphere touches . Calculate the force between two spheres and if distance between them is halved.
What is static electricity?
particle (nuclei of helium) falls per second on a neutral sphere. Calculate the time in which the sphere gets charged by .
A particle of mass has charge when it is at rest. When the particle moves with speed , charge on the particle will becomes ( is velocity of light in vacuum)
When a scale is rubbed with hair two electrons are transferred from scale to hair. Calculate the charge on hair or scale after transfer .
An object has an excess charge of . How many excess electrons does it have?
Two metallic spheres and of equal size each having charge and a third sphere of different size carries charge of . What will be the charge of sphere , if each of sphere and carries charge of after making contact between three spheres?
