Potential Due to a Electric Dipole
Potential Due to a Electric Dipole: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Potential Due to Dipole at Axial Point,Electric Potential Due Dipole at Equatorial Point,Electric Potential Due to Dipole at General Point etc.
Important Questions on Potential Due to a Electric Dipole
The electrostatic potential due to an electric dipole at an equatorial point is
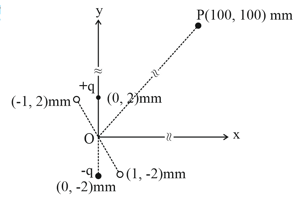
An electric dipole is formed by two charges and located in -plane at and , respectively, as shown in the figure. The electric potential at point due to the dipole is . The charges and are then moved to the points and , respectively. What is the value of electric potential at due to the new dipole?
Two equal charges of opposite sign separated by a distance constitute an electric dipole of dipole moment . If is a point at a distancefrom the centre of the dipole and the line joining the centre of the dipole to this point makes an angle with the axis of the dipole, then the potential at is given by: () (Where )
The electric field and the potential of an electric dipole vary with distance as
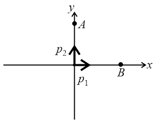
A charge moves from points to as shown in figure. If , then work done by electric force in moving charge from to , in the vicinity of two short dipoles placed at the origin with their dipole moments as shown, will be
A small dipole of dipole moment is placed at a distance from the centre of a neutral conducting sphere of radius The direction of dipole is towards the centre of the sphere. A tangent is drawn from the centre of dipole to the sphere which meets the sphere at point
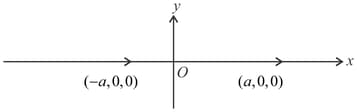
Two identical dipoles of dipole moment is a positive constant) are placed on axis at points and as shown. Then pick up the correct statements:
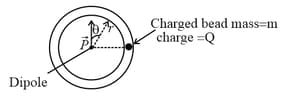
A small charged bead can slide on a circular frictionless, insulating wire frame. A point like dipole is fixed at the centre of circle, dipole moment is , initially the bead is on the plane of symmetric of the dipole. Bead is released from rest. Ignore the effect of gravity. Select the correct options.
The electric potential at the equatorial position due to the dipole is zero.
Electric potential at the equatorial point is
At which of the following points is the electric potential due to a dipole minimum?
The electrostatic potential due to an electric dipole at a distance varies as :
The distance between charges and is and between and is . The electrostatic potential at point at a distance from centre is , where the value of is ______. (Use )
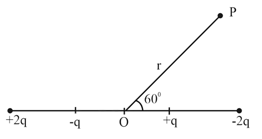
The electrostatic potential due to a short electric dipole at a distance varies as:
Two electric dipoles and are at points and separate by distance Find the distance from point where net electric potential is zero.
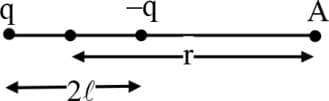
In the given dipole, for , the electric potential at will be
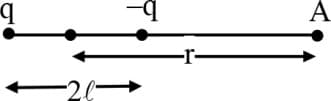
In given dipole, for , electric potential at will be
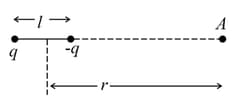
The given dipole has charges and separated by distance . The potential at due to dipole (assuming ) is
An electric dipole is fixed at the origin of coordinates. Its moment is directed in the positive -direction. A positive charge is moved from the point to the point by an external agent. In this process, the work done by the agent is
A short dipole is placed along -axis with centre at origin. The electric field at a point , which is at a distance from origin such that, makes an angle of with -axis, is directed along a direction making -
