Newton's Law of Cooling
Newton's Law of Cooling: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Newton's law of cooling, Newton's law of cooling by calculus method, etc.
Important Questions on Newton's Law of Cooling
A body cools from to in minutes. The temperature of the surroundings is . The time it takes to cool from to is
A body cools in minutes from to . The temperature of the surrounding is . The temperature of the body after the next minutes will be
An object cools from to in minutes, when the surrounding temperature is . Then the time taken by the object to cool from to is
[Take ]
The temperature of a cylindrical conductor starts rising when connected across a battery. The conductor radiates to the surrounding from it's curved surface following Newton's law of cooling and finally it attains a steady state temperature, its temperature exceeding the ambient temperature by If the length of the conductor is reduced to times of the original length, keeping other conditions unchanged, the steady state temperature of the conductor exceeds the ambient temperature by
A metal cylinder of mass is heated electrically by a heater in a room at . The cylinder temperature rises uniformly to in and finally becomes constant at . Assuming Newton's Law of cooling is valid.
What does a cooling curve show?
What does rate of cooling depend on?
How do you calculate cooling curve?
Initially, the rate of coaling is higher and decreases as the temperature falls.
Newton's law of cooling holds good provided the temperature difference between body and surrounding is
The quantity of heat required to heat mole of a mono atomic gas through one degree at constant pressure is:
A brass boiler has a base area and thickness It boils water at the rate of when placed on a gas stove. Estimate the temperature of the part of the flame in contact with the boiler. Thermal conductivity of brass:
A body cools from to In 5 minutes. Calculate the time it takes to cool from to . The temperature of the surroundings is .
It is a valid _____ in the transfer of heat from a radiator to a room, the loss of heat through the wall of a room.
Where k is a positive constant depending upon the area and nature of the surface of the body .
Two identical beakers and contain equal volumes of two different liquids at each and left to cool down. Liquid in has density of and specific heat of while the liquid in has density and specific heat of . Which of the following best describes their temperature versus time graph schematically? (assume the emissivity of both the beakers to be the same)
If a piece of metal is heated to temperature and then allowed to cool in a room which is at temperature, the graph between the temperature of the metal and time will be closest to :
Hot water in a vessel kept in a room, cools from to in minutes, from to in minutes and from to in minutes. Then,
The circuit below is used to heat water kept in a bucket.
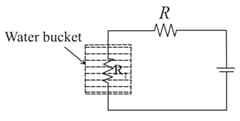
Assuming heat loss only by Newton's law of cooling, the variation in the temperature of the water in the bucket as a function of time is depicted by
A body cools down from to in time , from to in time and to in time . The correct statement according to Newtons law of cooling is
