First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as First Law of Thermodynamics, Polytropic Process, Adiabatic Process Examples, First Law of Thermodynamics in Isothermal Process, Heat in Isothermal Process and, First Law of Thermodynamics in Adiabatic Process
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics
An ideal gas is allowed to expand freely against vacuum in a rigid insulated container. The gas undergoes
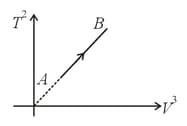
If an ideal diatomic gas follows the process as shown in graph, where is temperature in and is volume in , then molar heat capacity for this process will be [in terms of gas constant ],
A cycle tyre bursts suddenly. What is the type of this process?
A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a process . The heat given to the gas is,
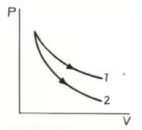
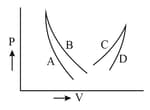
P-V plots for two gases during adiabatic processes are shown in the figure. Plots and should correspond respectively to:
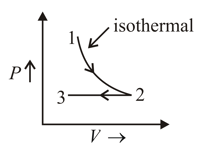
In adjoining diagram, no heat exchange between the gas and the surroundings will take place if the gas is taken along:
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is taken through a semicircular thermodynamic process shown in the diagram. The heat supplied to the system is
One mole of a mono-atomic gas undergoes the processes and as shown. The corresponding graph for the above process for moles of the gas is
A given mass of gas at a pressure and absolute temperature obeys the law during an adiabatic process. The adiabatic bulk modulus of the gas at a pressure is
The workdone on the system in changing the state of a gas adiabatically from equilibrium state to equilibrium state is . If the gas is taken from state to through another process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is , then the net workdone by the system in the later case is
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of If the system performs Work at a rate of joules per second, the rate at which internal energy changes is
Two cylinders and of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. is empty. Then the entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. After the gas reaches equilibrium the temperature of the gas measured. Which of the following is correct?
of water at , is completely converted to steam at , occupies . The increase in the internal energy of the molecules is:
(take the pressure , Latent heat of vaporisation )
An ideal monatomic gas with pressure , volume and temperature is expanded isothermally to a volume and a final pressure . If the same gas is expanded adiabatically to a volume , the final pressure is . The ratio is
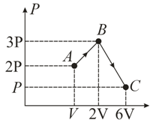
As shown in the figure, the amount of heat absorbed along the path is and the amount of work done by the system is . If the amount of work done along the path is the amount of heat absorbed will be:
For an adiabatic expansion of ideal gas, the value of is equal to
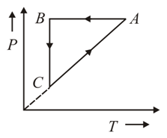
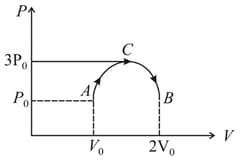
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken round the cyclic process as shown in figure then
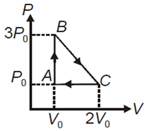
One mole of a monoatomic gas is brought from state to state along path Temperature at is Heat absorbed along path is equal to
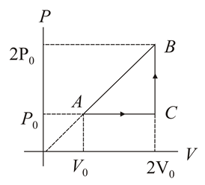
At two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas occupy a volume The gas expands adiabatically to a volume Calculate the final temperature of the gas.
[Given ]
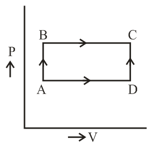
A cyclic process is shown in diagram. What would be its graph: