First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as First Law of Thermodynamics, Equation for Work Done and, Sign Convention in Thermodynamics
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics
An ideal gas is allowed to expand freely against vacuum in a rigid insulated container. The gas undergoes
If the temperature falls then is _____.
Work done by the gas or any system is always positive.
When heat is supplied to the system then is ____ and is ____ when heat is extracted from the system. Choose the appropriate option.
of rigid diatomic gas performs a work of when heat is supplied to it. The molar heat capacity of the gas during this transformation is The value of is ________ .
A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a process . The heat given to the gas is,
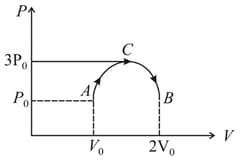
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is taken through a semicircular thermodynamic process shown in the diagram. The heat supplied to the system is
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of If the system performs Work at a rate of joules per second, the rate at which internal energy changes is
of water at , is completely converted to steam at , occupies . The increase in the internal energy of the molecules is:
(take the pressure , Latent heat of vaporisation )
As shown in the figure, the amount of heat absorbed along the path is and the amount of work done by the system is . If the amount of work done along the path is the amount of heat absorbed will be:
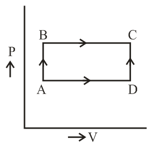
When a system is taken from state to state along the path , it is found that and . Along the path , . Work (in ) along the path is-
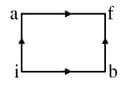
In thermodynamic process pressure of a fixed mass of gas is changed in such a manner that the gas releases joule of heat and joule of work was done on the gas. If the initial internal energy of the gas was joule, then, the final internal energy (in J) will be:
A thermodynamic process is shown in the figure. The pressures and volumes corresponding to some points in the figure are: and . In process of heat is added to the system and in process of heat is added to the system. The change in internal energy(in ) of the system in the process would be,
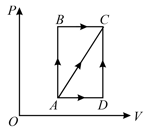
In a cyclic process, change in internal energy is zero.
A closed vessel in volume, contains a diatomic gas under a pressure of . What amount of heat should be imparted to the gas to increase the pressure in the vessel by five times?
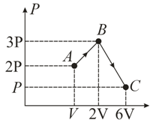
Two moles of helium gas undergo a cyclic process as shown. Assuming the gas to be ideal, the difference in heat absorbed and heat rejected by the gas is . Write the value of .
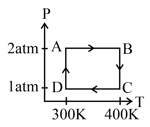
The molar heat capacity for the process is , where is gas constant, when of heat added to a monoatomic ideal gas, then gas performs a work of on its surrounding, then is.
Which one of the following is not true in a thermodynamic process?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. The heat exchanged by the engine with the surroundings at constant volume is: (, and are the pressures of the gas at point and point respectively, and is the volume of the gas at point )
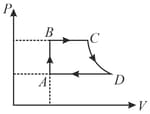
When the state of a gas adiabatically changed from an equilibrium state to another equilibrium state an amount of work done on the system is . If the gas is taken from state to via a process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is , the word done by the substance will be
