First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as First Law of Thermodynamics, Polytropic Process, Adiabatic Process Examples, Non-cyclic process, First Law of Thermodynamics in Isothermal Process and, First Law of Thermodynamics in Adiabatic Process
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics
Two moles of a monoatomic gas undergoes an isobaric process. If the gas temperature is increased by then the heat absorbed by the gas is (Take )
During adiabatic expansion, the increase in the volume is associated with
A system of gas at NTP is suddenly compressed to of its volume. Calculate the final temperature of the gas.
[Take ]
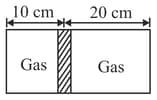
Diagram shows a horizontal cylindrical container of length , which is partitioned by a tight-fitting separator. The separator is diathermic but conducts heat very slowly. Initially the separator is in the state shown in the diagram. The temperature of left part of cylinder is and that on right part is . Initially the separator is in equilibrium. As heat is conducted from right to left part, separator displaces to the right. Find the displacement of separator after a long when gases on the two parts of cylinder are in thermal equilibrium.
An ideal gas is allowed to expand freely against vacuum in a rigid insulated container. The gas undergoes
A polyatomic gas follows a law constant. Find for which the heat exchange of gas in the process becomes zero
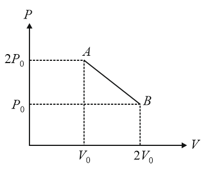
moles of an ideal gas undergoes a process as shown in the figure. The maximum temperature of the gas during the process will be:
The ratio of work done by an ideal monoatomic gas to the heat supplied to it in an isobaric process is
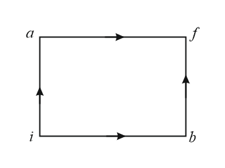
When a system is taken from state to state along the path , it is found that and . Along the path , and along the path is
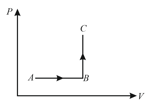
The diagram of a system undergoing thermodynamic transformation is shown in figure. The work done by the system in going from is and heat is given to the system. The change in internal energy between and is
Find the amount of work done to increase the temperature of one mole of ideal gas by , if it is expanding under the condition .
Two moles of a monatomic ideal gas are taken through a cyclic process shown on the diagram. The process is represented as = constant. If the efficiency of the given cyclic process is , then what is the value of ?
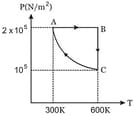
of rigid diatomic gas performs a work of when heat is supplied to it. The molar heat capacity of the gas during this transformation is The value of is ________ .
When the temperature of a body is equal to that of the surroundings then the body appears
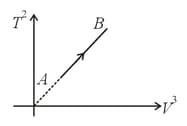
If an ideal diatomic gas follows the process as shown in graph, where is temperature in and is volume in , then molar heat capacity for this process will be [in terms of gas constant ],
When the temperature of a body is equal to that of the surroundings then the body appears
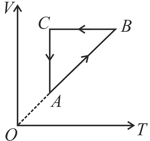
A thermodynamic cycle of an ideal gas is shown in the figure. Choose the correct option which represents the same cycle.
A cycle tyre bursts suddenly. What is the type of this process?
