Energy of an Orbiting Satellite
Energy of an Orbiting Satellite: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Kinetic Energy of Satellites, Gravitational Potential Energy of Satellites and, Conservation of Total Energy in Satellites
Important Questions on Energy of an Orbiting Satellite
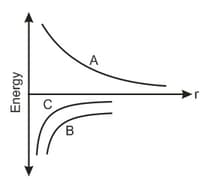
The figure shows the variation of energy with the orbit radius of a body in circular planetary motion. Find the correct statement about the curves A, B and C
When a satellite revolves in an elliptical orbit, its
The gravitational potential energy of a satellite revolving around the earth in circular orbit is Find the additional energy (in ) that should be given to the satellite so that it escapes from the gravitational field of earth. Assume earth's gravitational force to be the only gravitational force on the satellite and no atmospheric resistance.
Two satellites and have masses and respectively. is in a circular orbit of radius and is in a circular orbit of radius around the earth. The ratio of their kinetic energies, is
For a satellite orbiting very close to earth's surface, total energy is
An artificial satellite moving in a circular orbit around the earth has a total () energy . Its potential energy and kinetic energy respectively are
What is the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass from the surface of a planet of mass and in a circular orbit with an altitude of ?
A satellite of mass which is initially at rest,on earth surface is launched into a circular orbit of double the radius of earth. The radius of earth is . The minimum energy required to do so,is
A satellite is moved from one circular orbit around the earth, to another orbit of lesser radius. Which of the following statements is true ?
Suppose earth's orbital motion around the sun is suddenly stopped. Find the time (in days) taken by the earth to fall into the sun.
The satellites when launched from the earth are not given an orbital velocity initially. A multi-stage rocket propeller carries the spacecraft up to its orbit and during each stage rocket has been fired to increase the velocity to acquire the desired velocity for a particular orbit. The last stage of the rocket brings the satellite in circular/elliptical (desired) orbit. Consider a satellite of mass 150 kg in a low circular orbit. In this orbit, we cannot neglect the effect of air drag. This air opposes the motion of satellite and hence the total mechanical energy of earth-satellite system decreases. That means the total energy becomes more negative and hence the orbital radius decreases which causes the increase in kinetic energy. When the satellite comes in the low energy orbit, excessive thermal energy generation due to air friction may cause the satellite to burn up. Based on the above information, answer the following question.
If due to air drag, the orbital radius of the earth decreases from to . Then, the change in is:
The satellites when launched from the earth are not given an orbital velocity initially. A multi-stage rocket propeller carries the spacecraft up to its orbit and during each stage rocket has been fired to increase the velocity to acquire the desired velocity for a particular orbit. The last stage of the rocket brings the satellite in circular/elliptical (desired) orbit. Consider a satellite of mass 150 kg in a low circular orbit. In this orbit, we cannot neglect the effect of air drag. This air opposes the motion of satellite and hence the total mechanical energy of earth-satellite system decreases. That means the total energy becomes more negative and hence the orbital radius decreases which causes the increase in kinetic energy. When the satellite comes in the low energy orbit, excessive thermal energy generation due to air friction may cause the satellite to burn up. Based on the above information, answer the following question.
If due to air drag, the orbital radius of the earth decreases from to . Then, the change in kinetic energy is:
The satellites when launched from the earth are not given an orbital velocity initially. A multi-stage rocket propeller carries the spacecraft up to its orbit and during each stage rocket has been fired to increase the velocity to acquire the desired velocity for a particular orbit. The last stage of the rocket brings the satellite in circular/elliptical (desired) orbit. Consider a satellite of mass 150 kg in a low circular orbit. In this orbit, we cannot neglect the effect of air drag. This air opposes the motion of satellite and hence the total mechanical energy of earth-satellite system decreases. That means the total energy becomes more negative and hence the orbital radius decreases which causes the increase in kinetic energy. When the satellite comes in the low energy orbit, excessive thermal energy generation due to air friction may cause the satellite to burn up. Based on the above information, answer the following question.
It has been mentioned in the passage that as decreases, decreases but increases. The increase in is: [ total mechanical energy, orbital radius, kinetic energy]
In the graph shown, the potential energy of the earth-satellite system is shown by a solid line as a function of distance (the separation between the earth's centre and satellite). The total energy of the two objects which may or may not be bounded to the earth is shown in the figure by dotted lines. Mark the correct statement(s).
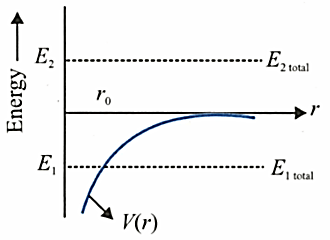
At perihelion, the mechanical energy of Pluto's orbit has:
A satellite is orbiting around the earth in a circular orbit of radius . Its
The period of moon's rotation around the earth is nearly days. If moon's mass were fold its present value, and all other things remain unchanged, the period of moon's rotation would be nearly
An artificial satellite moving in a circular orbit around the earth has a total (kinetic + potential) energy , its potential energy is
A satellite has kinetic energy potential energy and total energy . Which of the following statement is true?
Satellite has mass and orbital radius Satellite has mass and orbital radius The ratio of kinetic energy of satellite and will be:
