Newton's Third Law of Motion
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Newton's Third Law of Motion, Action and Reaction and, External and Internal Forces
Important Questions on Newton's Third Law of Motion
Ten coins each of mass are placed one above the other. The reaction force exerted by coin from the bottom on the coin is _____.
()
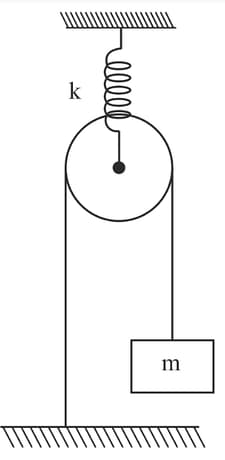
Consider the situation shown in figure. Masses of both the block and the pulley is . Assume that string and spring are light, the elongation of the spring at equilibrium is
The frictional force is an example of internal force.
Magnetic force is example of _____ force.
Which one of given force is not example of internal force?
Which of the given force is not external force?
Can a single isolated force exist in nature? Explain your answer.
Why is it not possible to push a car from inside?
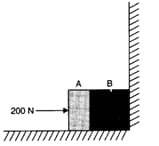
Two bodies A and B of masses and in contact with each other rest on a table against a rigid wall as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the bodies and the table is . A force of is applied horizontally to A. What are:
(a) the reaction of the partition?
(b) the action-reaction forces between A and B?
What happens when the wall is removed? Does the answer to (b) change, when the bodies are in motion? Ignore the difference between and .
Action and reaction _____ act on the same body.
(Choose from: can/cannot)
Newton’s third law of motion can be derived as a second special case of Newton’s _____ law of motion.
Which theory of motivation emphasizes the role of external rewards and punishments?
What role does 'reinforcement' play in the learning process?
Assertion: Nuclear force doesn't obey Newton's third law.
Reason: Nuclear force is not a central force.
Assertion: The third law of motion concludes that the forces occur in pairs of action and reaction.
Reason: The action force is more than the reaction force.
Assertion: Newton's third law is not applicable for nuclear forces.
Reason: Nuclear forces are short-ranged.
