Position Vector, Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
Position Vector, Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Acceleration Vector of an Object in 2D Motion,Components of Acceleration Vector of an Object in 2D Motion,Velocity Vector of an Object in 2D Motion, etc.
Important Questions on Position Vector, Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
A body of moves in the plane under the action of a force given by Assuming that the body is at rest at time the velocity of the body at is:
The position vector of a particle is The velocity of the particle is:
A football player is moving southward and suddenly turns eastward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player while turning is :
If tangential acceleration vector of a speeding up particle atis find the angle
A particle is moving in a straight line such that its velocity is increasing at per meter. The acceleration of the particle is _____ at a point where its velocity is .
A particle attached to a light wire of length is projected horizontally with a velocity of . Calculate its net acceleration when wire becomes horizontal.
Displacement of a particle in periodic motion is expressed as . If the time period of particle motion is , then displacement of the particle in will be
Displacement of a particle is given . Find its velocity vector.
The position vector of a particle is given by . What is the angle between initial velocity and initial acceleration?
A particle moves in the X-Y plane with a constant acceleration of in the direction making an angle of with the X-axis. At the particle is at the origin and its velocity is along the X-axis. Find the velocity and the position of the particle at .
A particle moves along a straight line such that its velocity at any time is given by , where is in seconds. Total distance travelled by the particle in first second is
The position of an object changes from in . Find its average velocity.
If the position of the particle is given by then find the velocity and the acceleration at .
On an open ground, a boy follows a track that turns to his left by an angle of after every . Starting from a given turn, the displacement of the boy at the fourth turn will be
A ring of radius is initially at the coordinate plane such that it touches the positive sides of the and axes at and respectively. The ring starts rolling at a speed of along the positive -axis. The coordinates of the point after minutes and seconds are
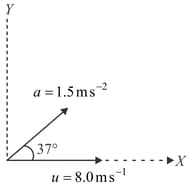
A particle moves in the plane with a constant acceleration of in the direction making an angle of with the -axis. At the particle is at the origin and its velocity is along the -axis. Find the velocity and the position of the particle at .
A particle is moving on a circular path of radius with uniform, speed . What is the displacement of the particle after it has described an angle of ?
A particle moves in a straight line so that distance where is time, then the acceleration is proportional to
Three particles and are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. They start moving with equal speeds (remains constant during the whole motion) such that always heads towards towards & towards . Finally they meet at a point. Find out the angle by which the line connecting and rotates with respect to initial orientation in space by the time distance between and reduces to half of the initial distance between and .
In plane a particle is displaced from a point to a point in . Find the displacement of the particle and its average velocity in vector form in the given time interval.
