Projectile Motion
Projectile Motion: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like 2D Motion,Horizontal Range of a Projectile from a Horizontal Plane,Horizontal Projectile Motion from a Height, etc.
Important Questions on Projectile Motion
A ball is projected at an angle of above with the horizontal from the top of a tower and strikes the ground in at angle of with the horizontal. Find the height of the tower and the speed with which it was projected.
A particle is projected in the X-Y plane. after projection, the velocity of the particle makes an angle with the X-axis. after projection, it moves horizontally. Find the velocity of projection (use )
A rifle with a muzzle velocity of shoots a bullet at a small target away in the same horizontal line. How high above the target must the gun be aimed so that the bullet will hit the target?
Two bodies of same mass are projected with the same velocity at an angle and respectively. The ratio of their horizontal ranges will be
The maximum range of a gun of horizontal terrain is . If then, muzzle velocity of a shell must be
From a high building, a stone is dropped and simultaneously another identical stone is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of Which one of the following statements is true?
A bullet is fired horizontally from a gun with a speed of in order to hit a target away. From what height above the target should the gun be aimed? (The resistance of air is negligible and ,
Two guns situated on the top of a hill of height fire one shot each with the same speed at some interval of time. One gun fires horizontally and other fires upwards at an angle of with the horizontal. The shots collide in air at point . Find the time interval between the firings.
A body is projected at an angle of with me horizontal with a speed of . What is the angle with horizontal after ?
A stone is thrown horizontally from the top of a high building with a speed of . It hits the ground at a distance from the building. Taking and neglecting air resistance will give :
Two Particles and are projected simultaneously from the two towers of height and . Particle is projected with an initial speed of at an angle of with the horizontal while particleis projected horizontally with speed . If they collide in air, what is the distance between the towers (Take )
.A magpie, flying horizontally at a speed of , drops a coin it is holding in its beak. The coin touches the ground with a speed equal to . At what height does the magpie fly approximately?
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion and the other is labelled as Reason
Assertion A: When a body is projected at an angle its range is maximum.
Reason R: For maximum range, the value of sin should be equal to one.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The trajectory of projectile, projected from the ground is given by . Where and are measured in meter. The maximum height attained by the projectile will be.
Which of the following quantities remain constant during projectile motion?
A particle is projected at an angle of with ground with speed . The speed of the particle after is (use )
A cart moves with a constant speed along a horizontal circular path. From the cart a body is thrown vertically up, with respect to the cart. The body will:
(a) land outside the circular path
(b) land somewhere on the path.
(c) follow a parabolic path
(d) follow an elliptical path
Which of the above statements are correct?
An object is projected in the air with initial velocity at an angle . The projectile motion is such that the horizontal range , is maximum. Another object is projected in the air with a horizontal range half of the range of first object. The initial velocity remains same in both the case. The value of the angle of projection, at which the second object is projected, will be
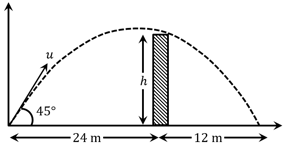
The angle of projection is . The heightis
A ball is thrown by a player from above ground level, clears the high wall placed from the player. If the angle of projection of the ball is , then determine the initial velocity of the ball.