Position, Path Length and Displacement
Position, Path Length and Displacement: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Kinematics, Position of Body, Motion and Rest, Reference Frames, Position - Time Graphs, Displacement of Body, Basic Definitions of Motion and, Distance as Path Length
Important Questions on Position, Path Length and Displacement
The study of motion without regard to forces that cause it is known as
What is kinematics in physics?
Three balls, and are released and all reach the point (shown in the figure). Balls and are released from two identical structures, one kept on the ground and the other at height from the ground as shown in the figure. They take time and respectively to reach (time starts after they leave the end of the horizontal portion of the structure). The ball is released from a point at height vertically above and reaches in time . Choose the correct statement.
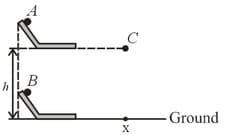
A drunkard is walking along a straight road. He takes steps forward and steps backward and so on. Each step is long and takes . There is a pit on the road away from the starting point. The drunkard will fall into the pit after .
Select the correct option for the object having a straight line motion represented by the following graph
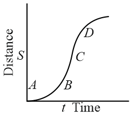
The maximum instantaneous velocity in the above distance- time graph of a particle is around the point
Position - time graph for motion with zero acceleration is
If a man goes towards north and towards east, then his displacement is
The and coordinates of a particle moving in a plane are given by and where, and are positive constants of appropriate dimensions and is time. Then, which of the following is not true?
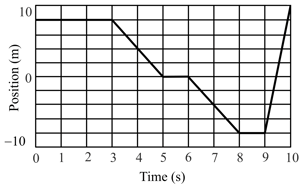
The position versus time graph of a particle moving along a straight line is shown. What is the total distance travelled by the particle from to
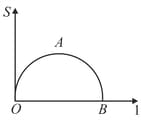
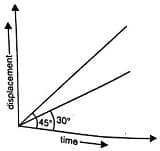
The displacement-time graph of two particles A and B are straight lines making angles of respectively with the time-axis. If the velocity of A is and that of B is then the value of is
The graph of displacement time for a body travelling in a straight line is given. We can conclude that
The displacement time graph of two moving particles make angles of with the x - axis. The ratio of the two velocities is
Assertion: The position-time graph of a body moving uniformly is a straight line parallel to position-axis.
Reason: The slope of position-time graph in a uniform motion gives the velocity of an object.
Assertion: Displacement of a body may be zero when distance travelled by it is not zero.
Reason: The displacement is the longest distance between initial and final position.
Graphs I and II give coordinates x(t) and y(t) of a particle moving in the x-y plane, starting from rest. Acceleration of the particle is constant and the graphs are drawn to the same scale. Which of the vector shown in options best represents the acceleration of the particle :
(I)  (II)
(II) 
An aeroplane flies 400m north and 300m south and then flies 1200m upwards, then net displacement is
An aeroplane flies 400m north and 300m south and then flies 1200m upwards, then net displacement is
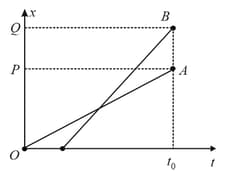
The position-timegraphs for two children and returning from their school to their homes and respectively along a straight path (taken as -axis) are shown in the figure below. Choose the incorrect option.
A body moves with a constant velocity of from the point in a direction of . The position vector of the body at is :
