Conservative Force and Potential Energy
Conservative Force and Potential Energy: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Potential Energy, Mechanical Energy, Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Stable Equilibrium, Conservative and Non-conservative Forces, Neutral Equilibrium, Unstable Equilibrium and, Energy Stored in Spring
Important Questions on Conservative Force and Potential Energy
A rubber ball is dropped from a height of on a plane, where the acceleration due to gravity is not shown. On bouncing, it rises to . The ball loses its velocity on bouncing by a factor of . Write value of .
Which one of the following is not a conservative force?
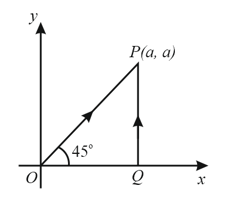
A particle is moved from to under a force from two paths. Path is and path is . Let and be the work done by this force in these two paths. Then,
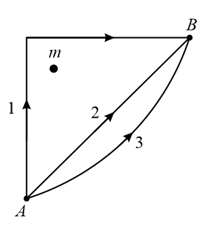
If and represent the work done in moving a particle from to along three different paths and , respectively (as shown), in the gravitational field of a point mass , find the correct relation between and .
Which of the following forces is not conservative?
The of a particle of mass moving along the - axis is given by, , where is in . It can be concluded that the wrong option is
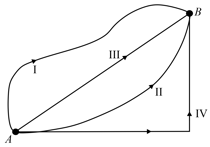
In a gravitational force field a particle is taken from to along different paths as shown in figure. Then
Assertion: Friction is a conservative force.
Reason: Friction does not depend upon mass of the body.
Frictional force is_______________.
Which of the following statement is not true?
The potential energy of a system increases if work is done
The potential energy of a particle is determined by the expression , where is a positive constant. The particle begins to move from a point with coordinates , only under the action of the potential field force. Then its kinetic energy at the instant when the particle is at a point with the coordinates is
The shape of the potential energy vs displacement curve for a spring is:
Which of the following is true for an Unstable equilibrium ?
A block of mass in the Fig. moving on the frictionless horizontal surface collides with the spring of spring constant
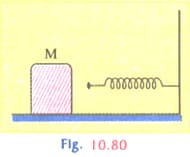
and compresses it by length . The maximum momentum of the block after collision is
Example of a non-conservative force is:
The shape of the potential energy versus displacement graph for an ideal spring-block system is:
Plots of potential energy vs displacement and kinetic energy vs displacement for an ideal spring-block system intersect each other:
A spring long is stretched by the application of a force. If force required to stretch the spring through , then work done in stretching the spring through is
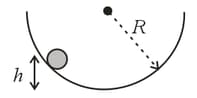
A small ball is pushed from a height along a smooth hemispherical bowl. With what speed should the ball be pushed so that it just reaches the top of opposite end of the bowl? The height of the top of the bowl is .