Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Laws of Reflection of Light,Reflection of Light,First Law of Reflection, etc.
Important Questions on Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
A luminous point object is placed at , whose images is formed at as shown in the figure. is the optical axis. Which of the following statements are correct?
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
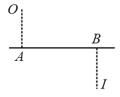
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

The reflection surface of a plane mirror is vertical. A particle is projected in a vertical plane which is also perpendicular to the mirror. The initial velocity of the particle is 10 m/s and the angle of projection is 60o. The point of projection is at a distance 5 m from the mirror. The particle moves towards the mirror. Just before the particle touches the mirror the velocity of approach of the particle and its image is:
A large temple has a depression in one wall. On the floor plan, it appears as an indentation having a spherical shape of radius . A worshipper stands on the centreline of the depression, out from its deepest point, and whispers a prayer. Where is the sound concentrated after reflection from the black wall of the depression?
If object is at distance from silvered plano convex lens whose refractive index is . Image is also formed at a distance of. What is radius of curvature: (Consider it is a thin lens)
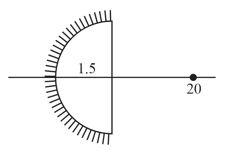
Where should an object long be placed in front of a convex mirror of focal length to obtain an image long.
A concave mirror has a focal length of . Determine the position of the object for which an erect and four times the size of the object image is formed. Draw relevant ray diagram.
The distance between a convex mirror and a plane mirror is . An object is kept in front of them at a distance of from the convex mirror. If both the mirrors form the image at the same place then calculate the focal length of the convex mirror.
A high object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror. The distance of the object from the mirror is , and its image is formed from the mirror, on the same side of the mirror as the object. Find the height of the image formed.
A rod of length lies along the principal axis of the concave mirror of focal length in such a way that the end of the rod which is closer to the pole is away from it. Calculate the length of the image.
Where should a point source be placed in front of a concave mirror so that reflected rays become parallel to principal axis?
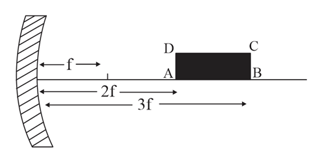
A rectangle is kept in front of a concave mirror of focal length with its corners and being, respectively, at distances and from the mirror with along the principal axis as shown in the figure. It forms an image in front of the mirror. What is the ratio of to ?
An object is moving with in front of a convex mirror () as shown in figure. Find speed of image if the mirror is stationary
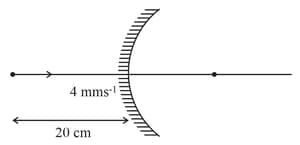
A source of light is at from a convex mirror and is then moved to a distance of from the mirror. How much does the image move, if the radius of curvature of the mirror is ?
A candle is placed away from a convex mirror of focal length . Give the location of the image and the magnification.
Derive the mirror equation for convex mirror.
Find the angle of deviation (both clockwise and anti clock wise) suffered by a ray incident on a plane mirror, (as shown in figure) at an angle of incidence .
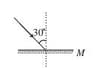
If a plane mirror is rotated in its own plane through an angle of keeping the incident ray direction fixed, then the angle through which the reflected ray turns is
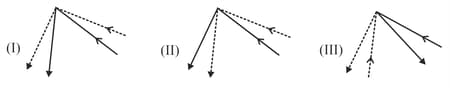
Each of these diagrams is supposed to show two different rays being reflected from the same point on the same mirror. Which option is correct :-