Mirror Formula
Mirror Formula: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Mirror Formula
Important Questions on Mirror Formula
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
A large temple has a depression in one wall. On the floor plan, it appears as an indentation having a spherical shape of radius . A worshipper stands on the centreline of the depression, out from its deepest point, and whispers a prayer. Where is the sound concentrated after reflection from the black wall of the depression?
An object is placed at from the concave mirror of focal length the nature of the image and magnification will be
An object of length is kept on the principal axis of a convex mirror at a distance of . The size of the image formed is-
An object of length is kept on the principal axis of a convex mirror at a distance of . The size of the image formed is-
A concave mirror of focal length produces an image times the size of the object. If the image is real, then the distance of the object from the mirror is
The relation between magnification , the object distance and focal length of the mirror is
A small candle, in size is placed at in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature . Find focal length of the mirror. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
A point object is kept on the principal axis at a distance from the focus of a concave mirror. If image is formed at from the focus of the mirror, then the distance of the focus from the pole of the mirror is
An object is placed at from the concave mirror of focal length the nature of the image and magnification will be
An object is present on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length Object is kept at a distance of from the mirror. If the velocity of object is towards mirror and velocity of mirror is towards object, then what must have been the velocity of image at the same instant ?
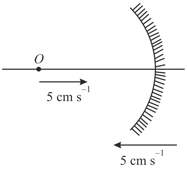
What is the size of the image when a short linear object of length b lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length f at a distance u from the pole.
Magnitude of relative velocity of object w.r.t. the image:
A particle moves in a circle of certain radius with a constant angular velocity. A concave mirror of focal length is placed with its principal axis passing through the centre of the circle and perpendicular to its plane. The distance between the pole of the mirror and the centre of the circle is . The ratio of acceleration of image to that of object is:
A point of object is placed at the centre of a glass sphere of radius 6 cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance of the virtual image from the surface of the sphere is
A tall object is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length What is the size and nature of the image?
An object is placed at a distance 20 cm from the pole of a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm. The image is produced.
Assertion: The formula connecting u, v and f for a spherical mirror is valid only for mirrors whose sizes are very small compared to their radii of curvature.
Reason: Laws of reflection are strictly valid for plane surfaces, but not for large spherical surfaces.
A point object is placed at a distance of and its real image is formed at a distance of from a concave mirror. If the object is moved by towards the mirror, the image will shift by about
