Spherical Mirrors
Spherical Mirrors: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Concave Mirror, Convex Mirror, Spherical Mirror, Focal Length of Concave Mirror, Focal Length of Convex Mirror, Magnification in Concave Mirror, Focal Length of Mirror and, Pole of Spherical Mirror
Important Questions on Spherical Mirrors
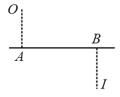
A luminous point object is placed at , whose images is formed at as shown in the figure. is the optical axis. Which of the following statements are correct?
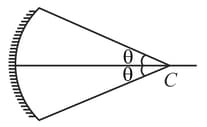
The circular boundary of the concave mirror subtends a cone of half angle at its centre of curvature. The minimum value of for which ray incident on this mirror parallel to the principle axis suffers reflection more than one is
A point source of light is 60 cm from a screen and is kept at the focus of a concave mirror which reflects light on the screen. The focal length of the mirror is 20 cm. The ratio of average intensities of the illumination on the screen when the mirror is present and when the mirror is removed is:
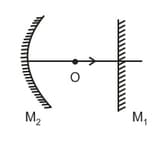
In the figure shown if the object 'O' moves towards the plane mirror, then the image I (which is formed after successive reflections from M1 & M2 respectively) will move:
A luminous point object is moving along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm towards it. When its distance from mirror is 20 cm its velocity is 4 cm/s. The velocity of the image in cm/s at that instant is:
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length . The near end of the rod is at a distance from the mirror. Its image will have a length
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

A thin road of length d/3 is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length = d such that its image, which is real and elongated, just touches the rod. Find the length of the image?
Which of the following statement is correct while using the mirror equation , when the object is kept on the left side of the mirror on the principal axis?(use real positive sign convention)
Focal plane of a spherical mirror is parallel to the principal axis of the mirror.
The centre of a sphere of which the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is a part is called
Mirror having a curved reflecting surface are called as spherical mirrors.
Mirror having a curved reflecting surface are called as_____ mirrors.
Which of the following can not produce a virtual image?
A boy is trying to start a fire by focusing sunlight on a piece of paper using an concave mirror of radius of curvature The diameter of the sun is and its mean distance from the earth is What is the diameter of the sun's image on the paper?
The radius of curvature of a convex spherical mirror is How far away from the mirror is an object, if the distance between its virtual image and the mirror is What is the height of the image?
[Apply formula for paraxial rays]
Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature along its optical axis is observed to move from to in second. What is the average speed of the object?
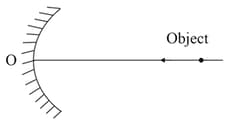
A point object is moving along principal axis of a concave mirror with uniform velocity towards pole. Initially the object is at infinite distance from pole on right side of the mirror as shown. Before the object collides with mirror, the number of times at which the distance between object and its image is are.
A rod of length lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length in such a way that its end closer to the pole is away from the mirror. The length of the image is :-
A point source is moving with a speed of in plane as shown. The radius of curvature of a concave mirror is What will be velocity vector of the image formed by paraxial rays

