Huygens Wave Theory of Light
Huygens Wave Theory of Light: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Wave Optics, Spherical Wavefront, Phase of Waves, Plane Wavefront, Cylindrical Wavefront, Secondary Wavelets, Huygens Wave Principle, Sources of Light Waves and, Types of Wave Fronts
Important Questions on Huygens Wave Theory of Light
How phenomenon of interference is explained on the basis of Haugen's theory?
How did Huygens' principle explained the law of reflection?
Which of the following phenomenon cannot be explained by the Huygens' wave theory?
State Huygen's principle. Using Huygen's wave theory, prove the laws of reflection.
Two sources of monochromatic light are said to be coherent, if light waves produced by them have the same
Fine rectangular slit is an example of _____ wavefront.
What is the shape of the wavefront when light is diverging from a point source?
Light waves travel in vacuum along the -axis. Which of the following may represent the wavefront?
The figure shows a surface separating two transparent media. Medium and medium . The lines and represent wave fronts of a light wave travelling in medium and incident on . The lines and represent wavefronts of the light wave in medium after refraction.
Light travels as a,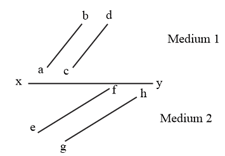
The figure shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium-I and medium-II. The lines ab and cd represents wave fronts of a light wave travelling in medium-I and incident on XY. The lines ef and gh represent wave fronts of light wave in medium-II after refraction the Speed of light is
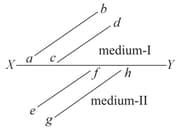
The figure shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium-I and medium-II. The lines ab and cd represents wave fronts of a light wave travelling in medium-I and incident on XY. The lines ef and gh represent wave fronts of light wave in medium-II after refraction the
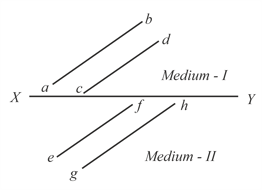
The phase of the light wave at c, d, e and f are respectively. It is given that , then
A wavefront is represented by the plane The propagation of wave takes place at
Venus looks brighter than other stars, due to
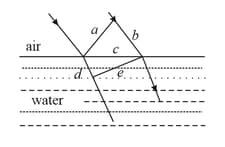
In the figure shown plane waves are refracted from air to water using Huygen's principle are lengths on the diagram. The refractive index of air with respect to water is in the ratio.
A monochromatic plane wave of speed c and wavelength is diffracted at a small aperture. The diagram illustrates successive wavefronts (vibrating in the same phase). After what time will some portion of the wavefront reach ?
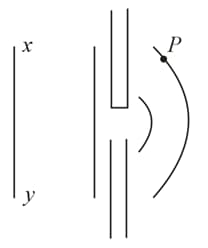
In which of the following cases we obtain a plane wavefront ?
A wave front is represented by the plane . The propagation of wave takes place at
