Spring - Block System
Spring - Block System: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Spring - Block System, Reduced Mass in SHM, Angular Frequency by Force Method, Angular Frequency by Energy Method, Rotational SHM with Spring Block and, Angular Frequency with Real Spring
Important Questions on Spring - Block System
For the oscillations exhibited by the spring block system on the smooth surface along the spring, the time period is equal to
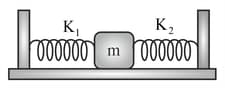
In the figure given below, a block of mass placed on a frictionless table is connected with two springs having same spring constant (). If the block is horizontally displaced through then the number of complete oscillations it will make in seconds will be
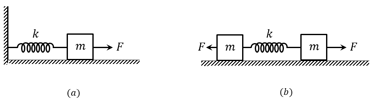
The figure (a) show a spring of force constant clamped rigidly at one end and a mass m attached to its free end. A forceapplied at the free end stretches the spring. The figure (b) shows the same spring with both ends free and attached to a mass at either end. Each end of the spring in (b) is stretched by the same force
a) What is the maximum extension of the spring in two cases?
b) If the mass in (a) and the two masses in (b) are released what is the period of
oscillation in each case.
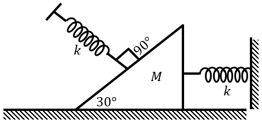
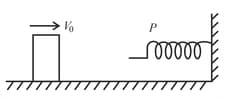
If there is no friction between wedge and ground, for small displacement of wedge on the ground, time period of its oscillation is:
A block of mass '' moving with velocity on a smooth horizontal surface strikes a spring fixed in vertical wall as shown in the figure. If maximum compression in the spring is , then spring constant of the spring will be
A body of mass performs linear SHM. The force constant of motion is . When the body is at a distance of from the equilibrium position has velocity of . Then the total energy of body will be
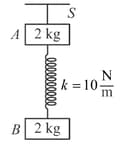
The system shown in figure is in equilibrium. The spring is light, the acceleration of both the blocks (in ) just after the string is cut is:
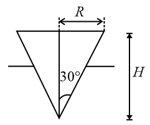
A cone with half the density of water is floating in water as shown in figure. It is depressed down by a small distance and released. The frequency of simple harmonic oscillations of the cone is
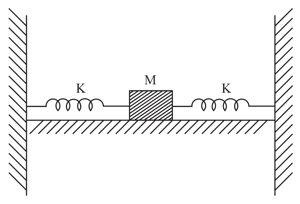
When the system shown in the diagram is in equilibrium, the right spring is stretched by . The coefficient of static friction between the blocks is . There is no friction between the bottom block and the supporting surface. The force constants of the springs are and . The blocks have equal mass of . each.
Find the maximum amplitude (in ) of the oscillations of the system shown in the figure that does not allow the top: block to slide on the bottom.
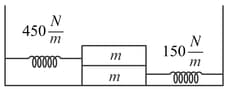
Given system is in equilibrium. All surfaces are smooth. Spring is ideal and blocks are sticked at the ends of spring. Now is removed. Average normal contact force between wall and mass upto the time spring attains its natural length for the first time in Newton is: (Given that Newton)
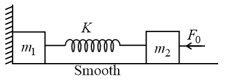
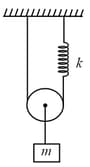
On displacing the mass in the arrangement shown below frequency of vertical oscillations will be (, , pulley is frictionless)
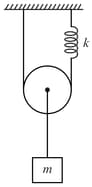
On displacing the mass in the arrangement shown below frequency of vertical oscillations will be (, pulley is frictionless)
In the system shown in figure, time period of oscillation is given by , where is
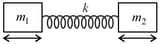
A mass hangs in equilibrium from a spring of constant . Another mass of is placed over . Find the new amplitude of oscillation after wards (in ) (Take )
When a block of mass is connected to a spring the time period recorded is seconds. When block is removed and a block of mass is attached to the same spring, it is observed that the block is oscillating with a time period of seconds. Then block is removed and a block of mass is attached to the same spring. It is observed that the block is oscillating with a time period of seconds. If all the three blocks and are taken together and connected across the same spring then the new time period of the composite system will be
A body of mass is suspended from a spring of spring constant . Another body of mass moving vertically upward with hits it and gets embedded in it. If amplitude is . find ''.
Two identical metal balls connected at the ends of a light spring of force constant form a dumbbell like structure. The dumbbell rests on a frictionless horizontal floor and third identical ball is placed at distance from the right ball of the dumbbell. All the three balls are in a line. A fourth identical ball moving with velocity collides with left ball of the dumbbell. If all collisions are elastic and rightmost ball acquires a velocity The minimum value of is Find
Two mass springs having spring constants and are connected in parallel as shown. The mass displaced from its equilibrium position and released. Find the expression for resultant frequency of oscillation.
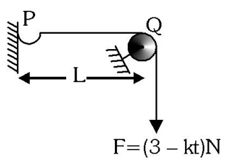
In the given figure, a string of linear mass density and length , is stretched by a force , where is a constant and is time in sec. At the time , a pulse is generated at the end of the string. Find the value of
(in ) if the value of force becomes zero as the pulse reaches point .
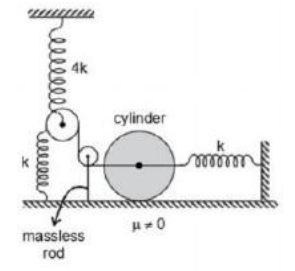
A cylinder of mass and radius is attached to a massless spring-pulley system as shown in the figure and all the spring are in their natural length at . The friction is sufficient to cause pure rolling of the cylinder. What is the time period (in ) of cylinder for small horizontal displacement? (spring constant and )