Ideal Gas Laws
Ideal Gas Laws: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, Avogadro's Law, Gay-Lussac's Law, Universal Gas Constant, Isotherm, Ideal Gas Assumptions, Random Motion of Gas Molecules and, Elastic Collisions between Molecules
Important Questions on Ideal Gas Laws
At constant volume pressure of a gas is directly proportional to temperature of the gas.
At a fixed pressure, when the volume is varied, the volume-temperature relationship traces a straight line .
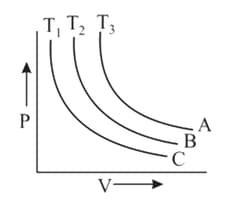
The PV diagram for three different isothermal processes A, B and C are shown above. Chose the correct option.
Using the assumptions made in kinetic theory of gases, derive an expression for pressure acting on the wall of a container by an ideal gas.
Volume of a real gas is negligible as compared to the volume of the container.
The collision between the molecules of an ideal gas is perfectly elastic.
Which one of the following correctly defines an ideal gas?
The volume of air in a car tyre is about at a temperature of and pressure .
Calculate the number of molecules in the tyre( in no. of Molecules).
A container of an ideal gas that is isolated from its surroundings is divided into two parts. One part has double the volume of the other. The pressure in each part is and the temperature is the same. The partition is removed. What is the pressure in the container now?
