- Written By
Akanksha P John
- Last Modified 28-01-2025
Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements: Properties and Uses
Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements: A chemical property describes a substance’s ability to undergo a specific chemical change. However, unlike physical properties, chemical properties can only be observed while the substance is being transformed into another substance.
The elements in the \({\rm{s}}\) and \({\rm{p}}\) blocks of the periodic table are known as representative elements or main group elements. Elements in groups \(1\) and \(2\) are classified as \({\rm{s}}\)-block elements, while elements in groups \(13\) to \(18\) are classified as \({\rm{p}}\)-block elements.
In this article, we will study all about the chemical properties and uses of a group in the \({\rm{p}}\)-block that is group \(15\)- Nitrogen family.
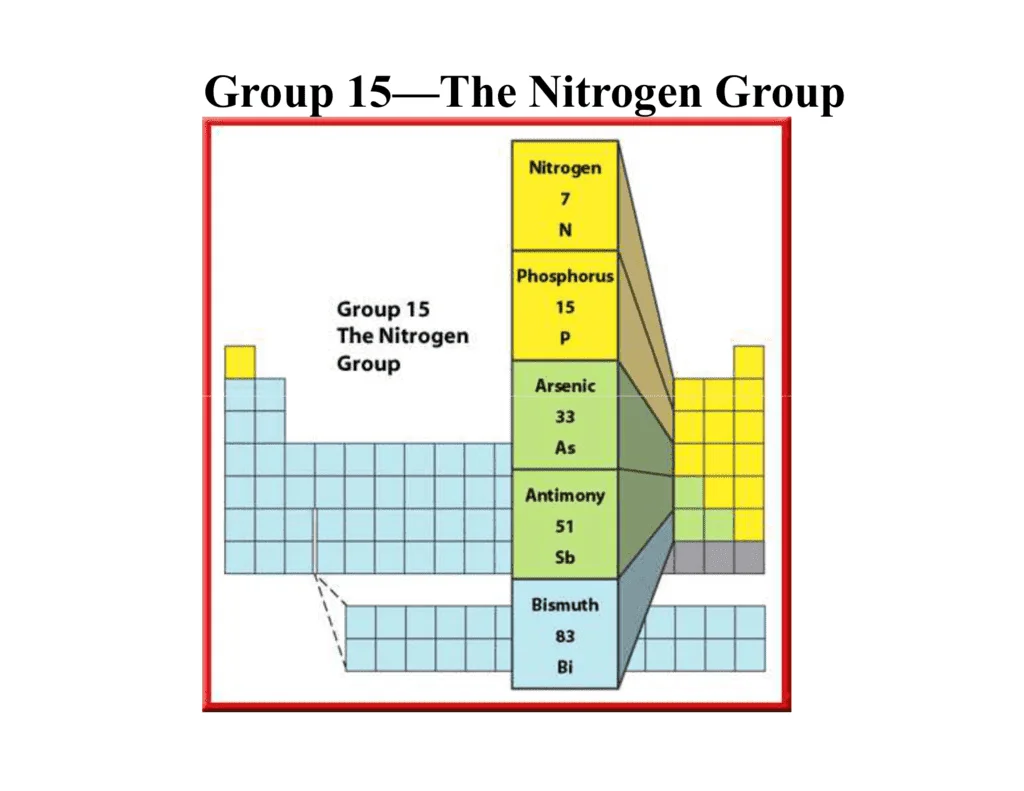
Group 15 Elements
The \({\rm{p}}\)-block elements are placed on the right-hand side of the periodic table from group \(13\) to \(18.\)
Group \(15\) is called the nitrogen family, and it includes five elements which are nitrogen \(\left( {\rm{N}} \right),\) phosphorus \(\left( {\rm{P}} \right),\) arsenic \(\left( {{\rm{As}}} \right),\) antimony \(\left( {{\rm{Sb}}} \right)\) and bismuth \(\left( {{\rm{Bi}}} \right).\)
Occurrence of Group 15 Elements
Nitrogen: \({\rm{78\% }}\) by volume of air. It is the most important member of this group and exists in form as a diatomic gas, \({{\rm{N}}_2}.\) Phosphorus is a mineral that is found in both animal and plant matter. Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA contain phosphate groups. Phosphates make up approximately \({\rm{60\% }}\) of the composition of bones and teeth.
Phosphoproteins can be found in egg yolk, milk, and bone marrow. The group’s remaining elements, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth, are mostly found as sulphide ores. Some examples include stibnite, arsenopyrite, and bismuth glance.
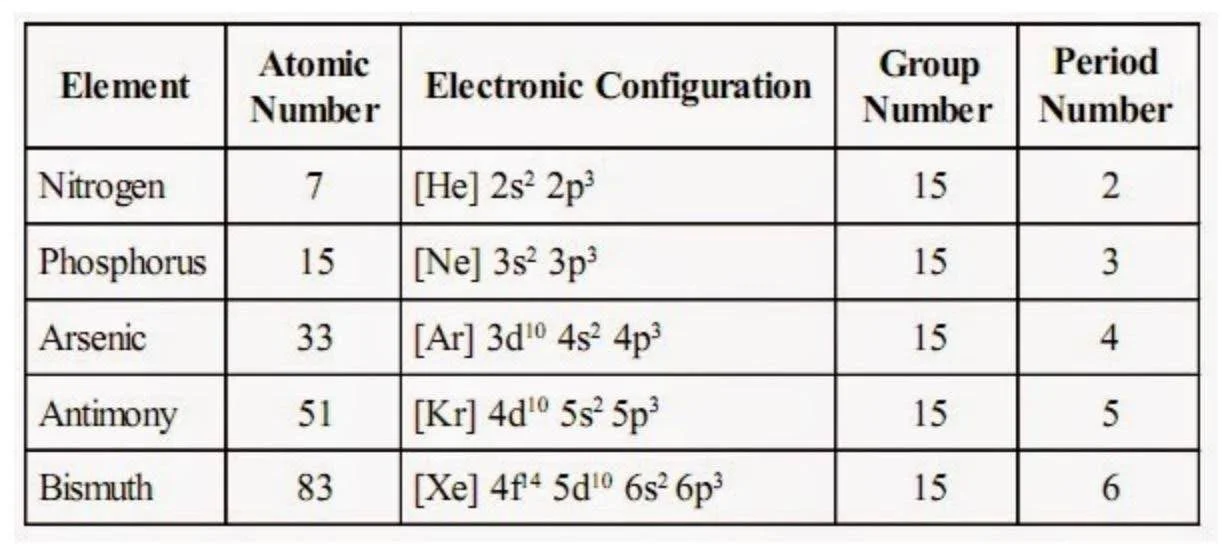
Electronic Configuration of Group 15 Elements
The elements of group \(15\) have five electrons in their valence shell, and the general electronic configuration for group \(15\) is \({\rm{n}}{{\rm{s}}^2}{\rm{n}}{{\rm{p}}^3}.\)
Chemical Properties of Group 15
Some of the chemical properties of Group \(15\) elements are as follows:
Oxidation States
This group’s elements have \(5\) electrons in their outermost shell and range in oxidation state from \(-3\) to \(+5.\)
The basic negative oxidation state of these elements is \(- 3.\) As one moves down the group, the tendency to exhibit \(- 3\) oxidation state decreases. This is because the atomic size and metallic character have increased.
Group \(15\) elements have positive oxidation states of \(+3\) and \(+5\) due to the formation of covalent bonds. The stability of the \(+5\) oxidation state decreases as one moves down the group due to the inert pair effect, while the stability of the \(+3\) oxidation state increases.
Nitrogen’s valence shell is made up entirely of \({\rm{s}}\)- and \({\rm{p}}\)-orbitals, with no \({\rm{d}}\)-orbitals. As a result, the maximum covalency of nitrogen is \(4.\) An atom or ion of nitrogen can achieve a covalency of four by sharing its lone pair of electrons with another atom or ion.
Phosphorus and the remaining elements can have a covalency of five and a maximum covalency of six, which is referred to as expanded covalency. This is possible due to the presence of vacant \({\rm{d}}\)-orbitals in the valence shell. Compounds with a \(+5\) oxidation state in group fifteen are all covalent.
Reaction With Hydrogen
When any substance reacts with hydrogen, it produces hydrides. For example, whenever group \(15\) elements react, they form hydrides of the formula \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{H}}_3},\) which are as follows:
\(\mathop {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}}\limits_{{\rm{Ammonia}}} \,\,\mathop {{\rm{P}}{{\rm{H}}_3}}\limits_{{\rm{Phosphine}}} \,\mathop {{\rm{As}}{{\rm{H}}_3}}\limits_{{\rm{Arsine}}} \,\mathop {{\rm{Sb}}{{\rm{H}}_3}}\limits_{{\rm{Stibine}}} \,\mathop {{\rm{Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}}\limits_{{\rm{Bismuthine}}} \)
All of these hydrides are known as Lewis bases. These can be made by reacting metal nitrides or metal phosphide with water, which is as follows:
(i) When magnesium nitride reacts with water, it forms magnesium hydroxide and ammonia.
\({\rm{M}}{{\rm{g}}_3}{{\rm{N}}_2} + 6{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{O}} \to 3{\rm{Mg}}{\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right)_2} + 2{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(ii) Likewise, for the preparation of phosphine, calcium phosphide reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and phosphine.
\({\rm{C}}{{\rm{a}}_3}{{\rm{P}}_2} + 6{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{O}} \to 3{\rm{Ca}}{\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right)_2} + 2{\rm{P}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
The properties of hydrides are-
Bond Angle
The bond angle decreases as one moves down the group. The order of decreasing angle is as follows:
\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{P}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{As}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{Sb}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(i) The reason for this is that as the size of the central atom increases, the lone pair will push closer to the bond pair-bond pair. As a result, the bond angle decreases.
(ii) Basic character: It refers to a molecule’s ability to donate its lone pair. The order of decreasing basic character is as follows:
\(\begin{array}{l} {\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{P}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{As}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{Sb}}{{\rm{H}}_3} > {\rm{Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\\ {\rm{Most}}\,{\rm{basic}}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\rm{Least}}\,{\rm{basic}} \end{array}\)
Because of the large size of the bismuth, the lone pair density is less close to the bismuth, and thus the tendency to lose electrons decreases.
Stability
The size comparability of hydrides determines their stability. The order of stability of hydrides is as follows:
\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > P}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > As}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > Sb}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(i) As the size increases, bond length increases, bond dissociation energy decreases, and thus stability decreases.
Reducing Nature
The reducing character of hydrides is listed in the following order:
\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ < P}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ < As}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ < Sb}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ < Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(i) In the case of \({\rm{Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3},\) the bond strength is low so it can easily give hydride ion, hence the reducing character of \({\rm{Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\) is the highest.
Boiling Point
The boiling point is determined by the Vander waal force, which increases with increasing size.
The boiling points of \(15\) group hydrides are listed in the following order:
\({\rm{Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > Sb}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > As}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > P}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(i) Because of hydrogen bonding, ammonia has a higher boiling point than phosphine in the case of \({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\) and \({\rm{P}}{{\rm{H}}_3}.\)
Solubility
The solubility of hydrides in water for group \(15\) is:
\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > P}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > As}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > Sb}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{ > Bi}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(i) Ammonia has a higher solubility due to hydrogen bond formation.
Reaction With Oxygen
Whenever group \(15\) elements react with oxygen, they form oxides with formula \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3}\) and \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}\) where \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3}\) is trioxides and \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}\) is pentoxides.
Nitrogen can form a wide range of different oxides, ranging from \(+1\) to \(+5. \) Nitrogen oxides have the following oxidation states:
1. \({{\rm{N}}_2}{\rm{O}}\) (laughing gas) oxidation state \(+1.\)
2. \({\rm{NO}}\) has an oxidation state \(+2.\)
3. \({{\rm{N}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3}\) has an oxidation state of \(+3.\)
4. \({{\rm{N}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_4}\) has an oxidation state of \(+4\)
5. \({{\rm{N}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}\) has an oxidation state of \(+5.\) (most acidic)
\({\rm{p\pi }} – {\rm{p\pi }}\) bonding occurs in all of the oxides.
1. Phosphorus forms oxide in \(+3\) oxidation state \(\left( {{{\rm{P}}_4}{{\rm{O}}_6}} \right),\, + 4\) oxidation state \(\left( {{{\rm{P}}_4}{{\rm{O}}_8}} \right),\) and \(+5\) oxidation state \(\left( {{{\rm{P}}_4}{{\rm{O}}_10}} \right).\)
2. \({\rm{A}}{{\rm{s}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3},\,{\rm{A}}{{\rm{s}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}\) are the oxides formed by \({\rm{As}}\) (Arsenic trioxide and Arsenic pentoxide).
3. \({\rm{Sb}}\) oxide is formed as \({\rm{S}}{{\rm{b}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3}\) and \({\rm{S}}{{\rm{b}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}\) (Antimony trioxide and Antimony pentoxide).
4. \({\rm{B}}{{\rm{i}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}\) and \({\rm{B}}{{\rm{i}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3}\) are the oxides formed by \({\rm{Bi}}\) (Bismuth trioxide and Bismuth pentoxide).
Nature of Oxides
1. Acidic oxides are formed by nitrogen and phosphorus.
2. Amphoteric oxide is formed by arsenic and antimony.
3. Bismuth oxidises to form basic oxide.
“The higher the oxidation state, the oxide will be more acidic.”
Reaction With Halogens
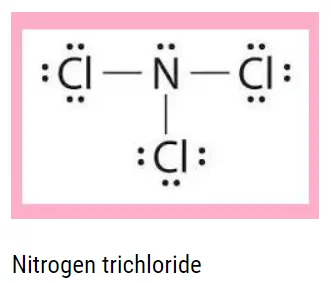
The elements of group \(15\) combine with halogen to form the halides of the general formula \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{X}}_3}\) and \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{X}}_5}.\) Nitrogen does not form pentahalides because the \({\rm{d}}\)-orbital is not available, but it does form trihalides. The trihalide structure is distorted tetrahedral of hybridization \({\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^3}.\)
The geometry is as follows:
Characteristics of Trihalides
1. They are covalent, and their stability increases as moving down the group.
2. Nitrogen trihalides are the least stable.
3. Nitrogen triflourides have the highest stability among trihalides of nitrogen.
The order of stability in decreasing order is-
\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{F}}_3}{\rm{ > NC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}{\rm{ > NB}}{{\rm{r}}_3}{\rm{ > N}}{{\rm{I}}_3}\)
The reason for sizes being incomparable is-
4. Phosphorus trihalides, arsenic trihalides, and antimony trihalides are good lewis bases.
5. Because of the inert pair effect, the stability of group \(15\) trihalides increases as they move down the group.
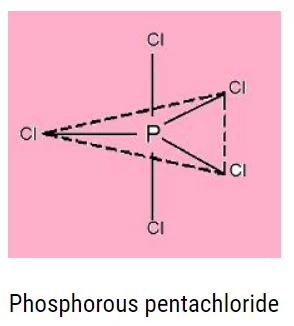
Characteristics of Pentahalides
- \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{X}}_5}\) is their general formula.
- Their hybridization is \({\rm{ds}}{{\rm{p}}^3}.\)
Pentahalides have a trigonal bipyramidal geometry, as shown below:
3. Because of the inert pair effect, the group stability of pentahalides decreases as one moves down the group.
4. All pentahalides are lewis acids.
All the elements of group \(15\) combine with metals to form their binary compounds in which the elements show a \(-3\) oxidation state.
For example: Nitrogen form nitrides (\({\rm{M}}{{\rm{g}}_3}{{\rm{N}}_2}:\) magnesium nitride), phosphorus form phosphide (\({\rm{C}}{{\rm{a}}_3}{{\rm{P}}_2}:\)calcium phosphide) Arsenic forms arsenides (\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}_3}{\rm{As}}:\)sodium arsenide), antimony forms antimonides (\({\rm{Z}}{{\rm{n}}_2}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{b}}_3}:\)zinc antimonide) and bismuth forms bismuthides (\({\rm{M}}{{\rm{g}}_3}{\rm{B}}{{\rm{i}}_2}:\)magnesium bismuthides).
Anomalous Behaviour of Nitrogen
In general, the properties of a group’s principal element differ from those of the other elements. Nitrogen has properties that are distinct from those of other elements. The exceptional properties of nitrogen are attributed to Because of the following:
(i) Because of its small nuclear size,
(ii) High ionisation enthalpy and high electronegativity
(iii) The absence of \({\rm{d}}\)-orbitals,
(iv) Capability to form various bonds.
Uses of Group 15 Elements
The following are some examples of how to group \(15\) elements can be used:
(i) Nitrogen and phosphorus are two of the elements required for life to exist.
(ii) Nitrogen gas, \({{\rm{N}}_2},\) makes up the vast majority of the Earth’s atmosphere. Pnictides are diatomic pnictogen molecules. Because of their valence, pnictide atoms are linked by a covalent triple bond.
(iii) Phosphorus can be found in a wide range of products, including matches, fireworks, and fertiliser. It’s also used in the synthesis of phosphoric acid.
(iv) Arsenic is a poison. It has been used as a poison as well as a rodenticide.
(v) Alloys are made with antimony.
Summary of Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements
In this article, we studied in detail the chemical properties of group \(15\) elements which are called the nitrogen family or pnictogen. They have a general electronic configuration of \({\rm{n}}{{\rm{s}}^2}{\rm{n}}{{\rm{p}}^3}.\) The chemical properties can be summarized as follows-
(i) Group \(15\) elements form hydrides of the formula \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(ii) They form oxides of formula \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3}\) and \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}.\)
(iii) The elements of group \(15\) combine with halogen to form the halides of the general formula \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{X}}_3}\) and \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{X}}_5}.\)
FAQs on Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements
Q.1. What are the chemical properties of group 15 elements?
Ans: The chemical properties of group \(15\) elements are as follows-
(i) Group \(15\) elements form hydrides of the formula \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{H}}_3}\)
(ii) They form oxides of formula \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_3}\) and \({{\rm{E}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}.\)
(iii) The elements of group \(15\) combine with halogen to form the halides of the general formula \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{X}}_3}\) and \({\rm{E}}{{\rm{X}}_5}.\)
Q.2. Why do all group 15 elements have similar chemical properties?
Ans: The valence shell electronic configuration has a significant impact on how an element behaves. Group \(15\) elements have the valence electron shell configuration \({\rm{n}}{{\rm{s}}^2}{\rm{n}}{{\rm{p}}^3}.\) All the group \(15\) elements have the same arrangement, which is why they are similar.
Q.3. What is special about group 15 on the periodic table?
Ans: The group \(15\) elements are called nitrogen family or pnictogen and they have similar characteristics across the group.
Q.4. Name the elements of group 15.
Ans: Group \(15\) is called the nitrogen family and it includes five elements which are nitrogen \(\left( {\rm{N}} \right),\) phosphorus \(\left( {\rm{P}} \right),\) arsenic \(\left( {{\rm{As}}} \right),\) antimony \(\left( {{\rm{Sb}}} \right)\) and bismuth \(\left( {{\rm{Bi}}} \right).\)
Q.5. State the uses of group 15 elements.
Ans: The following are some examples of how to group \(15\) elements can be used:
(i) Nitrogen and phosphorus are two of the elements required for life to exist.
(ii) Nitrogen gas, \({{\rm{N}}_2}\) makes up the vast majority of the Earth’s atmosphere. Pnictides are diatomic pnictogen molecules similar to this one. Because of their valence, pnictide atoms are linked by a covalent triple bond.
(iii) Phosphorus can be found in a wide range of products, including matches, fireworks, and fertiliser. It’s also used in the synthesis of phosphoric acid.
(iv) Arsenic is a poison. It has been used as a poison as well as a rodenticide.
(v) Alloys are made with antimony.