- Written By
Akanksha P John
- Last Modified 29-01-2025
Lactose Formula: Introduction, Properties, Lactose Intolerance
Lactose Formula: Do you know what is common in milk, yoghurt, cheese, cottage cheese, beer, and whey powder? It is lactose.
This article is about the lactose formula, which is a disaccharide sugar made up of galactose and glucose subunits. Furthermore, lactose accounts for \(2 – 8\% \) (by weight) of milk. Lactose is a water-soluble solid that is white in colour. Furthermore, it is used in the food industry. We will explore in detail structure, properties, and lactose intolerance.
Introduction to Lactose
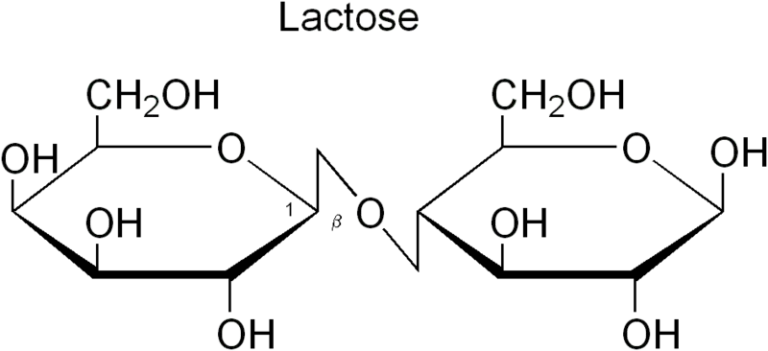
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of \(\beta -{\text{D}}\)-galactose and \(\beta -{\text{D}}\)-glucose molecules linked together by a \(\beta – \left({1 – 4} \right)\) glycosidic linkage. Lactose accounts for approximately \(2 – 8\% \) (by weight) of the solids in milk. The name is derived from the Latin word for milk, as well as the -ose suffix used to identify sugars. It has an empirical formula \({{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}\) and a molecular weight of \(342.3\,{\text{g}}/{\text{mol}}.\)
Study Citric Acid Formula Here
Source of Lactose
It is almost entirely synthesised in mammary glands of mammals (with the exception of whales and hippos) during the suckling period by a protein complex called lactose synthase, which is composed of lactalbumin (a milk protein) and galactosyltransferase; the latter catalyses the link of galactose to glucose present on lactalbumin.
It accounts for \(7.5\% \) and \(4.5\% \) of the composition of woman and cow’s milk, respectively, and provides approximately \(40\% \) of the energy that newborns obtain from mother milk; in adulthood, it accounts for \(5 – 10\% \) of dietary carbohydrates.
It is less soluble than other disaccharides and has a sweetness of \(16\% \) that of sucrose.
Bacterial fermentation converts it to lactic acid, which is responsible for the souring of milk.
The molecular formula for lactose is \({{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}.\) Lactose is a disaccharide that is formed by the condensation of galactose and glucose.
Properties of Lactose
- i. Lactose has a sweetness of \(0.2\) to \(0.4\) when compared to sucrose, which has a sweetness of \(1.0.\) In comparison, glucose has a sweetness of \(0.6\) to \(0.7,\) fructose has a sweetness of \(1.3,\) galactose has a sweetness of \(0.5\) to \(0.7,\) maltose has a sweetness of \(0.4\) to \(0.5,\) sorbose has a sweetness of \(0.4,\) and xylose has a sweetness of \(0.6\) to \(0.7.\)
- ii. Lactose has the same calorific value as other carbohydrates after being completely digested in the small intestine. Lactose, on the other hand, is not always completely digested in the small intestine. Lactose has a calorific value ranging from \(2\) to \(4\,{\text{kcal}}/{\text{g}},\) depending on the amount consumed, whether it is consumed with or without food, and the amount of lactase present in the intestines. Lactose that has not been digested serves as dietary fibre. It also has a positive effect on mineral absorption, such as calcium and magnesium.
- iii. Lactose has a glycemic index of \(46\) to \(65.\) In comparison, glucose has a glycemic index of \(100\) to \(138,\) sucrose has a glycemic index of \(68\) to \(92,\) maltose has a glycemic index of \(105,\) and fructose has a glycemic index of \(19\) to \(27.\)
- iv. Among sugars, lactose has a low cariogenicity (producing or promoting the development of tooth decay). This is because it is not a substrate for the formation of dental plaque and is not rapidly fermented by oral bacteria. Milk’s buffering capacity also reduces lactose’s cariogenicity.
Foods High in Lactose
Lactose-rich foods are those that contain milk. Ice cream, milk puddings, hot chocolate, eggnog, macaroni and cheese, yoghurt, pancakes, milk chocolate, cottage cheese, and mashed potatoes are all examples.
Applications of Lactose
Lactose has a variety of applications, including pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, and fermentation.
Lactose in Pharmaceuticals
Lactose is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug preparation and production. Whey, the liquid left after curdling and straining milk during the cheesemaking process, is used to make pharmaceutical-grade lactose.
Lactose is used as an excipient in the majority of its applications (inactive ingredient). Its primary function is to aid in the absorption of the active ingredient in the body.
Lactose can be found in approximately \(60 – 70\% \) of all pharmaceutical dosage forms, including capsules, tablets, syrups, creams, and pastes. Furthermore, approximately \(45\% \) of drugs contain a combination of lactose and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC).
Lactose in Food Processing
Lactose is used in a variety of food processing applications. Whey is also the primary source of edible lactose, which is used in food processing.
Because of its ability to carry colours and flavours well, it is used in seasonings and baked goodsIce cream, skim milk, condensed milk, dry soups, coffee creamers, chocolate and chocolates, meat products, and canned fruit and vegetables are all made with it. Lactose, when added to food, has the potential to reduce costs while also regulating sweetness.
Lactose in Fermentation
Lactose fermentation results in the production of cheese, yoghurt, kefir, and acidified (sour) milk. Lactose can also be fermented to produce lactic acid, which has a variety of applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries.
Fermentation is the addition of lactic acid bacteria (and, less commonly, yeast) to milk or a milk product.
Lactose in Identification of Bacteria
The ability of bacteria to ferment the lactose in the clinical laboratory may aid in determining which bacterial species is causing an ailment, such as food poisoning. Lactose is fermented by Escherichia coli, but not by the majority of Salmonella species.
Lactose in Cutting Agents
Lactose is frequently used as a cutting agent in illegal recreational drugs. Cutting agents are chemicals or medications that are used to dilute and bulk up recreational substances.
Cutting agents are often utilised in the manufacture of illegal drugs, and the materials used in this procedure are usually less expensive than the recreational drug itself.
Health Benefits of Lactose
Lactose has some advantages for babies’ health. Human breast milk contains \(7.2\% \) lactose, which provides up to half of the energy requirements of breastfeeding babies.
Lactose, which is found in human milk, aids in the development of microorganisms that live in babies’ digestive tracts. It also improves calcium absorption in babies.
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a disorder in which the body is unable to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and other dairy products. Stomach pain is the most common symptom of this illness.
Lactase enzymes normally aid in the breakdown of lactose. Lactose intolerance occurs when the body does not produce enough lactase. Lactose intolerance is very common, and it causes symptoms such as bloating, diarrhoea, cramps, and flatulence after consuming lactose-containing dairy products.
Lactose intolerance is not the same as lactose maldigestion. Lactose maldigestion reduces the activity of the lactase enzyme, making lactose digestion difficult. However, it produces few or no symptoms.
Lactase deficiency causes some babies to be born unable to digest lactose in breast milk or formula. Severe diarrhoea is the most common symptom of this type of lactose intolerance, and babies with this condition may become dehydrated and lose weight. The lactose-formula is frequently recommended.
The lactose-formula is usually made from cow’s milk that has been refined to remove the lactose and replace it with another type of sugar. Lactose-formulas use corn as a carbohydrate source rather than lactose.
Lactose-formulas are not the same as low-lactose formulas. They still contain lactose but at a lower concentration. The low-lactose formula may be a good choice for babies who are gassy, fussy, spit up a lot, or are in general discomfort.
In this article, we studied the chemical formula of lactose which is \({{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}.\) It is a disaccharide that is a sugar composed of galactose and glucose subunits. It is found in the mammary glands of mammals (with the exception of whales and hippos) during the suckling period by a protein complex called lactose synthase. We also studied that lactose finds its uses in the pharmaceutical industry, food processing, bacterial identification, and cutting agents. Now we also know about lactose intolerance which is the inability to digest lactose.
Lactose Formula MCQs
- Hydrolysis of lactose yields-
a.) glucose
b.) galactose
c.) sucrose
d.) Both (a) and (b)
Correct Answer- d
Hint- Lactose is a combination of two compounds.
- Lactose can be hydrolysed in the presence of which enzyme?
a.) lactase
b.) maltase
c.) sucrose
d.) lipases
Correct Answer- a
Hint- It is also known as β-galactosidase.
- Lactose can also be called as-
a.) milk sugar
b.) malt sugar
c.) cane sugar
d.) grape sugar
Correct Answer- a
Hint- Lactose is made of glucose and galactose.
- Lactose can be commonly found in –
a.) sugar cane
b.) sugar beet
c.) cereals
d.) mammals milk
Correct Answer- d
Hint- Lactase is produced during the suckling period.
- Lactose is a combination of glucose and-
a.) maltose
b.) galactose
c.) sucrose
d.) None of the above
Correct Answer- b
Hint- It is a monosaccharide.
- Which of the following is not a symptom of lactose intolerance?
a.) bloating
b.) cramps
c.) nausea
d.) fever
Correct Answer- d
Hint- Lactose intolerance in the inability to digest lactose which causes stomach problems.
- Which of the following is a food, someone with lactose intolerance might try?
a.) fresh milk
b.) buttermilk
c.) yoghurt
d.) powdered milk
Correct Answer- c
Hint- It is produced by bacteria.
- Which of the following statements is incorrect about lactose intolerance?
a.) Deficiency of lactase enzyme is associated with intolerance of milk
b.) It leads to flatulence
c.) Curd is better tolerated than milk in the tolerant individuals
d.) It is due to the deficiency of enzyme which converts galactose into glucose
Correct Answer- d
Hint- It is produced in our small intestine.
- The chemical formula of lactose is-
a.) C12H22O11
b.) C6H22O11
c.) C12H12O11
d.) C12H22O12
Correct Answer- a
Hint- Lactose is made of glucose and galactose.
Which of the following foods are high in lactose?
a.) ice cream
b.) eggnog
c.) cheese
d.) All of the above
Correct Answer- d
Hint- Lactose-rich foods are those that contain milk.
Q.1. What function does lactose play in the body?
Ans: Lactose is made up of two main components: glucose and galactose. These are the two simple sugars that your body uses directly as energy. Lactase, an enzyme in our bodies, converts lactose to glucose and galactose. Human milk can meet up to \(50\% \) of an infant’s energy requirements. Galactose has a variety of biological functions, including immunological and neural processes. Lactose may also aid in the absorption of calcium and other minerals such as copper and zinc, particularly during childhood. Lactose is used as a prebiotic or nutrient by the intestinal microbiota when it is not digested in the small intestine.
Q.2. What causes lactose intolerance?
Ans: Lactose is a natural sugar (or carbohydrate) found in milk and other dairy products. Our bodies contain a natural enzyme called lactase, which aids in the breakdown of lactose and the absorption of energy from it. The majority of people have difficulty in digesting lactose due to a decrease in lactase activity known as weaning, also known as lactase non-persistence. Furthermore, the genes that code for lactose become less active with age. Some people keep their ability to produce lactase, while others lose it after infancy. Lactose intolerance occurs when lactose maldigestion causes intestinal discomfort such as bloating.
Q.3. How long does it take for the lactose-formula to work?
Ans: It can also take up to two weeks to see results after switching from a regular cow’s milk formula to a lactose-formula. If a child has been diagnosed with lactose intolerance or galactosemia, parents should avoid other dairy products such as cheese and yoghurt when starting solids.
Q.4. What is the lactose-formula?
Ans: Lactose-formula is usually made from cow’s milk that has been refined to remove the lactose and replace it with another type of sugar. Lactose-formulas use corn as a carbohydrate source rather than lactose.
Q.5. What is the chemical formula for lactose?
Ans: The chemical formula for lactose is \({{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}.\)
Q.6. How is lactose formed? Explain with structural formula.
Ans: Lactose is a disaccharide composed of \(\beta -{\text{D}}\)-galactose and \(\beta -{\text{D}}\)-glucose molecules linked together by a \(\beta – \left({1 – 4} \right)\) glycosidic link. Lactose accounts for approximately \(2 – 8\% \) of the solids in milk. It has a chemical formula of \({{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}\) and the molecular weight of \(342.3\,{\text{g}}/{\text{mol}}\)
Q.7. What is the structural formula for the hydrolysis of lactose?
Ans: Lactose hydrolysis yields one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose.
\(\underset{{{\text{Lactose}}}}{\mathop {{{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{or}}\,{\text{Lactase}}}]{{{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }}}\underset{{{\text{D}} – \left( + \right) – {\text{Glucose}}}}{\mathop {{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_6}}} + \underset{{{\text{D}} – \left( + \right) – {\text{Galactose}}}}{\mathop {{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_{12}}{{\text{O}}_6}}} \)
Study About Camphor Formula Here
We hope this detailed article on the lactose formula will be helpful in your preparation. If you have any doubts related to the article or in general about the lactose formula, please reach out to us, and we will get back to you as soon as possible.